Segmental neurofibromatosis: a report of 3 cases
- PMID: 20418991
- PMCID: PMC2856359
- DOI: 10.4103/0019-5154.60366
Segmental neurofibromatosis: a report of 3 cases
Abstract
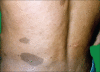
Neurofibromatosis is a genetic disorder of neural crest-derived cells that primarily affect growth of neural tissues. It is broadly divided into three categories: (a) von Recklinghausen's neurofibromatosis or NF-1, (b) bilateral acoustic neuroma (NF-2), and (c) all other neurofibromatoses, including alternate or atypical forms of the disease. The patients with generalized form of NF1 are characterized by multiple café-au-lait spots and neurofibromas and diagnosed easily. But when an individual has small number of lesions in a limited region of the body it could be neglected by the patient or not be recognized by the clinicians as a segmental form of neurofibromatosis. We describe three cases of segmental neurofibromatosis (SNF). These cases have been classified as segmental NF according to Riccardi's definition of SNF and classification of neurofibromatosis. Segmental form of NF may evolve into a complete form over time. Also, this disorder may be transmitted to the offspring's of these individuals. Hence genetic counseling of these individuals must include these facts.
Keywords: Segmental neurofibromatosis; café-au-lait spots; neurofibroma; neurofibromatosis 1.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures



References
-
- Theos A. American College of Physicians; American Physiological Society. Pathophysiology of neurofibromatosis type 1. Ann Intern Med. 2006;144:842–9. - PubMed
-
- Roth RR, Martines R, James WD. Segmental neurofibromatosis. Arch Dermatol. 1987;123:917–20. - PubMed
-
- Crowe FW, Schull WJ, Neel JV. A clinical, pathological and genetic study of multiple neurofibromatosis. Springfield, III: Charles C Thomas Publishers; 1956. pp. 74pp. 80–2.–139.pp. 153–9.
-
- Miller RM, Sparkes RS. Segmental neurofibromatosis. Arch Dermatol. 1977;113:837–8. - PubMed
-
- Riccardi VM. Neurofibromatosis: Clinical heterogeneity. Curr Probl Cancer. 1982;7:1–34. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
