Vimentin is a novel anti-cancer therapeutic target; insights from in vitro and in vivo mice xenograft studies
- PMID: 20419128
- PMCID: PMC2855704
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0010105
Vimentin is a novel anti-cancer therapeutic target; insights from in vitro and in vivo mice xenograft studies
Retraction in
-
Retraction: Vimentin Is a Novel Anti-Cancer Therapeutic Target; Insights from In Vitro and In Vivo Mice Xenograft Studies.PLoS One. 2019 Mar 21;14(3):e0214006. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0214006. eCollection 2019. PLoS One. 2019. PMID: 30897132 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
Background: Vimentin is a ubiquitous mesenchymal intermediate filament supporting mechano-structural integrity of quiescent cells while participating in adhesion, migration, survival, and cell signaling processes via dynamic assembly/disassembly in activated cells. Soft tissue sarcomas and some epithelial cancers exhibiting "epithelial to mesenchymal transition" phenotypes express vimentin. Withaferin-A, a naturally derived bioactive compound, may molecularly target vimentin, so we sought to evaluate its effects on tumor growth in vitro and in vivo thereby elucidating the role of vimentin in drug-induced responses.
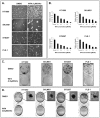
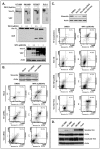
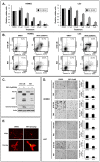
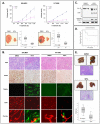
Methods and findings: Withaferin-A elicited marked apoptosis and vimentin cleavage in vimentin-expressing tumor cells but significantly less in normal mesenchymal cells. This proapoptotic response was abrogated after vimentin knockdown or by blockade of caspase-induced vimentin degradation via caspase inhibitors or overexpression of mutated caspase-resistant vimentin. Pronounced anti-angiogenic effects of Withaferin-A were demonstrated, with only minimal effects seen in non-proliferating endothelial cells. Moreover, Withaferin-A significantly blocked soft tissue sarcoma growth, local recurrence, and metastasis in a panel of soft tissue sarcoma xenograft experiments. Apoptosis, decreased angiogenesis, and vimentin degradation were all seen in Withaferin-A treated specimens.
Conclusions: In light of these findings, evaluation of Withaferin-A, its analogs, or other anti-vimentin therapeutic approaches in soft tissue sarcoma and "epithelial to mesenchymal transition" clinical contexts is warranted.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures




References
-
- Fletcher CDM UK, editor. Pathology and Genetics of Soft Tissue and Bone. Lyon, France: IARC Press; 2002. World Health Organization Classification of Tumors.
-
- Sorensen PH, Lynch JC, Qualman SJ, Tirabosco R, Lim JF, et al. PAX3-FKHR and PAX7-FKHR gene fusions are prognostic indicators in alveolar rhabdomyosarcoma: a report from the children's oncology group. J Clin Oncol. 2002;20:2672–2679. - PubMed
-
- de Alava E, Kawai A, Healey JH, Fligman I, Meyers PA, et al. EWS-FLI1 fusion transcript structure is an independent determinant of prognosis in Ewing's sarcoma. J Clin Oncol. 1998;16:1248–1255. - PubMed
-
- Hirota S, Isozaki K, Moriyama Y, Hashimoto K, Nishida T, et al. Gain-of-function mutations of c-kit in human gastrointestinal stromal tumors. Science. 1998;279:577–580. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

