PRP-17 and the pre-mRNA splicing pathway are preferentially required for the proliferation versus meiotic development decision and germline sex determination in Caenorhabditis elegans
- PMID: 20419786
- PMCID: PMC3097115
- DOI: 10.1002/dvdy.22274
PRP-17 and the pre-mRNA splicing pathway are preferentially required for the proliferation versus meiotic development decision and germline sex determination in Caenorhabditis elegans
Abstract
In C. elegans, the decision between germline stem cell proliferation and entry into meiosis is controlled by GLP-1 Notch signaling, which promotes proliferation through repression of the redundant GLD-1 and GLD-2 pathways that direct meiotic entry. We identify prp-17 as another gene functioning downstream of GLP-1 signaling that promotes meiotic entry, largely by acting on the GLD-1 pathway, and that also functions in female germline sex determination. PRP-17 is orthologous to the yeast and human pre-mRNA splicing factor PRP17/CDC40 and can rescue the temperature-sensitive lethality of yeast PRP17. This link to splicing led to an RNAi screen of predicted C. elegans splicing factors in sensitized genetic backgrounds. We found that many genes throughout the splicing cascade function in the proliferation/meiotic entry decision and germline sex determination indicating that splicing per se, rather than a novel function of a subset of splicing factors, is necessary for these processes.
Copyright (c) 2010 Wiley-Liss, Inc.
Figures
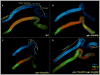
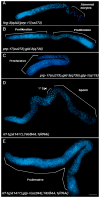
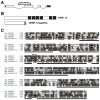



References
-
- Ahringer J, Kimble J. Control of the sperm-oocyte switch in Caenorhabditis elegans hermaphrodites by the fem-3 3′ untranslated region. Nature. 1991;349:346–348. - PubMed
-
- Austin J, Kimble J. glp-1 is required in the germ line for regulation of the decision between mitosis and meiosis in C. elegans. Cell. 1987;51:589–599. - PubMed
-
- Austin J, Kimble J. Transcript analysis of glp-1 and lin-12, homologous genes required for cell interaction during development of Caenorhabditis elegans. Cell. 1989;58:565–571. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

