siRNA delivery to CNS cells using a membrane translocation peptide
- PMID: 20420373
- PMCID: PMC2874326
- DOI: 10.1021/bc900488e
siRNA delivery to CNS cells using a membrane translocation peptide
Abstract
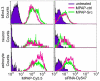
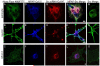
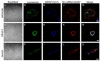
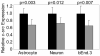
RNA interference (RNAi) is a sequence-specific gene silencing technique that has been applied to multiple pathological conditions. In this report, we describe the generation and in vitro characterization of an RNAi-based fluorescent probe for use as a therapeutic in the setting of ischemic stroke. Probe delivery to bEnd.3 brain endothelial cells and primary cortical neurons and astrocytes was promoted by incorporating small interfering RNA (siRNA) into complexes with fluorescently labeled myristoylated polyarginine peptides. The resulting probe was partially protected from serum nuclease degradation and was efficiently internalized by cells as confirmed by flow cytometry and confocal microscopy. In addition, application of the siRNA probe directed against c-Src, a protein implicated in stroke pathology, led to statistically significant reduction of endogenous c-src mRNA levels in all cell types tested. Results demonstrate the proof-of-principle that functionalized peptide--siRNA probes can be used as potential tools for dual imaging and therapeutic applications.
Figures


References
-
- Vives E, Brodin P, Lebleu B. A truncated HIV-1 Tat protein basic domain rapidly translocates through the plasma membrane and accumulates in the cell nucleus. J Biol Chem. 1997;272:16010–7. - PubMed
-
- Derossi D, Joliot AH, Chassaing G, Prochiantz A. The third helix of the Antennapedia homeodomain translocates through biological membranes. J Biol Chem. 1994;269:10444–50. - PubMed
-
- Schwarze SR, Ho A, Vocero-Akbani A, Dowdy SF. In vivo protein transduction: delivery of a biologically active protein into the mouse. Science. 1999;285:1569–72. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

