Acute exercise reduces hepatic glucose production through inhibition of the Foxo1/HNF-4alpha pathway in insulin resistant mice
- PMID: 20421289
- PMCID: PMC2911223
- DOI: 10.1113/jphysiol.2009.183996
Acute exercise reduces hepatic glucose production through inhibition of the Foxo1/HNF-4alpha pathway in insulin resistant mice
Erratum in
-
Erratum/Corrigendum.J Physiol. 2016 Sep 1;594(17):5031-2. doi: 10.1113/JP272728. Epub 2016 Jun 27. J Physiol. 2016. PMID: 27581572 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Expression of concern in
-
Expression of Concern.J Physiol. 2018 Oct;596(20):5063-5064. doi: 10.1113/JP277015. J Physiol. 2018. PMID: 30318697 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
Protein hepatocyte nuclear factor 4alpha (HNF-4alpha) is atypically activated in the liver of diabetic rodents and contributes to hepatic glucose production. HNF-4alpha and Foxo1 can physically interact with each other and represent an important signal transduction pathway that regulates the synthesis of glucose in the liver. Foxo1 and HNF-4alpha interact with their own binding sites in the phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase (PEPCK) and glucose-6-phosphatase (G6Pase) promoters, and this binding is required for their effects on those promoters. However, the effect of physical activity on the HNF-4alpha/Foxo1 pathway is currently unknown. Here, we investigate the protein levels of HNF-4alpha and the HNF-4alpha/Foxo1 pathway in the liver of leptin-deficient (ob/ob) and diet-induced obese Swiss (DIO) mice after acute exercise. The ob/ob and DIO mice swam for four 30 min periods, with 5 min rest intervals for a total swimming time of 2h. Eight hours after the acute exercise protocol, the mice were submitted to an insulin tolerance test (ITT) and determination of biochemical and molecular parameters. Acute exercise improved insulin signalling, increasing insulin-stimulated Akt and Foxo1 phosphorylation and decreasing HNF-4alpha protein levels in the liver of DIO and ob/ob mice under fasting conditions. These phenomena were accompanied by a reduction in the expression of gluconeogenesis genes, such as PEPCK and G6Pase. Importantly, the PI3K inhibitor LY292004 reversed the acute effect of exercise on fasting hyperglycaemia, confirming the involvement of the PI3K pathway. The present study shows that exercise acutely improves the action of insulin in the liver of animal models of obesity and diabetes, resulting in increased phosphorylation and nuclear exclusion of Foxo1, and a reduction in the Foxo1/HNF-4alpha pathway. Since nuclear localization and the association of these proteins is involved in the activation of PEPCK and G6Pase, we believe that the regulation of Foxo1 and HNF-4alpha activities are important mechanisms involved in exercise-induced improvement of glucose homeostasis in insulin resistant states.
Figures

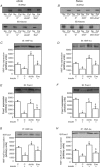
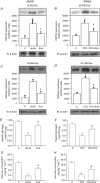
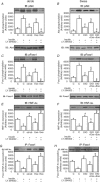
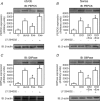
Comment in
-
Exercise: not just a medicine for muscle?J Physiol. 2010 Aug 1;588(Pt 15):2687-8. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2010.193797. J Physiol. 2010. PMID: 20675815 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Exercise: not just a medicine for muscle?J Physiol. 2010 Aug 1;588(Pt 15):2687-8. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2010.193797. J Physiol. 2010. PMID: 20675815 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Exercise training decreases mitogen-activated protein kinase phosphatase-3 expression and suppresses hepatic gluconeogenesis in obese mice.J Physiol. 2014 Mar 15;592(6):1325-40. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2013.264002. Epub 2014 Jan 6. J Physiol. 2014. PMID: 24396063 Free PMC article.
-
Irisin inhibits hepatic gluconeogenesis and increases glycogen synthesis via the PI3K/Akt pathway in type 2 diabetic mice and hepatocytes.Clin Sci (Lond). 2015 Nov;129(10):839-50. doi: 10.1042/CS20150009. Epub 2015 Jul 13. Clin Sci (Lond). 2015. PMID: 26201094
-
CREB and FoxO1: two transcription factors for the regulation of hepatic gluconeogenesis.BMB Rep. 2013 Dec;46(12):567-74. doi: 10.5483/bmbrep.2013.46.12.248. BMB Rep. 2013. PMID: 24238363 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeting Forkhead box O1 from the concept to metabolic diseases: lessons from mouse models.Antioxid Redox Signal. 2011 Feb 15;14(4):649-61. doi: 10.1089/ars.2010.3370. Epub 2010 Sep 16. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2011. PMID: 20615072 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
HIIT Ameliorates Inflammation and Lipid Metabolism by Regulating Macrophage Polarization and Mitochondrial Dynamics in the Liver of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Mice.Metabolites. 2022 Dec 21;13(1):14. doi: 10.3390/metabo13010014. Metabolites. 2022. PMID: 36676939 Free PMC article.
-
The intensity of IUGR-induced transcriptome deregulations is inversely correlated with the onset of organ function in a rat model.PLoS One. 2011;6(6):e21222. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0021222. Epub 2011 Jun 22. PLoS One. 2011. PMID: 21731679 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of hepatic TRB3/Akt interaction induced by physical exercise and its effect on the hepatic glucose production in an insulin resistance state.Diabetol Metab Syndr. 2015 Aug 18;7:67. doi: 10.1186/s13098-015-0064-x. eCollection 2015. Diabetol Metab Syndr. 2015. PMID: 26288661 Free PMC article.
-
Labeled breath tests in patients with NASH: Octanoate oxidation relates best to measures of glucose metabolism.Front Physiol. 2023 Apr 21;14:1172675. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2023.1172675. eCollection 2023. Front Physiol. 2023. PMID: 37153214 Free PMC article.
-
Chronic exercise increases plasma brain-derived neurotrophic factor levels, pancreatic islet size, and insulin tolerance in a TrkB-dependent manner.PLoS One. 2014 Dec 22;9(12):e115177. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0115177. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 25531651 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Altomonte J, Richter A, Harbaran S, Suriawinata J, Nakae J, Thung SN, Meseck M, Accili D, Dong H. Inhibition of Foxo1 function is associated with improved fasting glycemia in diabetic mice. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2003;285:E718–E728. - PubMed
-
- Anai M, Funaki M, Ogihara T, Terasaki J, Inukai K, Katagiri H, Fukushima Y, Yazaki Y, Kikuchi M, Oka Y, Asano T. Altered expression levels and impaired steps in the pathway to phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase activation via insulin receptor substrates 1 and 2 in Zucker fatty rats. Diabetes. 1998;47:13–23. - PubMed
-
- Aoi W, Ichiishi E, Sakamoto N, Tsujimoto A, Tokuda H, Yoshikawa T. Effect of exercise on hepatic gene expression in rats: a micro array analysis. Life Sci. 2004;75:3117–3128. - PubMed
-
- Barthel A, Schmoll D. Novel concepts in insulin regulation of hepatic gluconeogenesis. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2003;285:E685–692. - PubMed
-
- Bécard D, Hainault I, Azzout-Marniche D, Bertry-Coussot L, Ferré P, Foufelle F. Adenovirus-mediated overexpression of sterol regulatory element binding protein-1c mimics insulin effects on hepatic gene expression and glucose homeostasis in diabetic mice. Diabetes. 2001;50:2425–2430. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

