Macrophage alpha1 AMP-activated protein kinase (alpha1AMPK) antagonizes fatty acid-induced inflammation through SIRT1
- PMID: 20421294
- PMCID: PMC2885183
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M110.123620
Macrophage alpha1 AMP-activated protein kinase (alpha1AMPK) antagonizes fatty acid-induced inflammation through SIRT1
Abstract
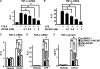
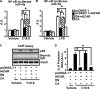
In this study, we aim to determine cellular mechanisms linking nutrient metabolism to the regulation of inflammation and insulin resistance. The nutrient sensors AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) and SIRT1 show striking similarities in nutrient sensing and regulation of metabolic pathways. We find that the expression, activity, and signaling of the major isoform alpha1AMPK in adipose tissue and macrophages are substantially down-regulated by inflammatory stimuli and in nutrient-rich conditions, such as exposure to lipopolysaccharide (LPS), free fatty acids (FFAs), and diet-induced obesity. Activating AMPK signaling in macrophages by 5-aminoimidazole-4-carboxamide-1-beta4-ribofuranoside or constitutively active alpha1AMPK (CA-alpha1) significantly inhibits; although inhibiting alpha1AMPK by short hairpin RNA knock-down or dominant-negative alpha1AMPK (DN-alpha1) increases LPS- and FFA-induced tumor necrosis factor alpha expression. Chromatin immunoprecipitation and luciferase reporter assays show that activation of AMPK by CA-alpha1 in macrophages significantly inhibits LPS- or FFA-induced NF-kappaB signaling. More importantly, in a macrophage-adipocyte co-culture system, we find that inactivation of macrophage AMPK signaling inhibits adipocyte insulin signaling and glucose uptake. Activation of AMPK by CA-alpha1 increases the SIRT1 activator NAD(+) content and SIRT1 expression in macrophages. Furthermore, alpha1AMPK activation mimics the effect of SIRT1 on deacetylating NF-kappaB, and the full capacity of AMPK to deacetylate NF-kappaB and inhibit its signaling requires SIRT1. In conclusion, AMPK negatively regulates lipid-induced inflammation, which acts through SIRT1, thereby contributing to the protection against obesity, inflammation, and insulin resistance. Our study defines a novel role for AMPK in bridging the signaling between nutrient metabolism and inflammation.
Figures
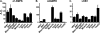
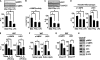

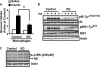
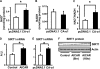

Similar articles
-
Omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids antagonize macrophage inflammation via activation of AMPK/SIRT1 pathway.PLoS One. 2012;7(10):e45990. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0045990. Epub 2012 Oct 5. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 23071533 Free PMC article.
-
Antagonistic crosstalk between NF-κB and SIRT1 in the regulation of inflammation and metabolic disorders.Cell Signal. 2013 Oct;25(10):1939-48. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2013.06.007. Epub 2013 Jun 11. Cell Signal. 2013. PMID: 23770291 Review.
-
Quercetin reduces obesity-associated ATM infiltration and inflammation in mice: a mechanism including AMPKα1/SIRT1.J Lipid Res. 2014 Mar;55(3):363-74. doi: 10.1194/jlr.M038786. Epub 2014 Jan 24. J Lipid Res. 2014. PMID: 24465016 Free PMC article.
-
The full capacity of AICAR to reduce obesity-induced inflammation and insulin resistance requires myeloid SIRT1.PLoS One. 2012;7(11):e49935. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0049935. Epub 2012 Nov 21. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 23183898 Free PMC article.
-
AMP-activated protein kinase inhibits NF-κB signaling and inflammation: impact on healthspan and lifespan.J Mol Med (Berl). 2011 Jul;89(7):667-76. doi: 10.1007/s00109-011-0748-0. Epub 2011 Mar 23. J Mol Med (Berl). 2011. PMID: 21431325 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Fumarates modulate microglia activation through a novel HCAR2 signaling pathway and rescue synaptic dysregulation in inflamed CNS.Acta Neuropathol. 2015 Aug;130(2):279-95. doi: 10.1007/s00401-015-1422-3. Epub 2015 Apr 29. Acta Neuropathol. 2015. PMID: 25920452 Free PMC article.
-
Metabolic Inflammation-Differential Modulation by Dietary Constituents.Nutrients. 2016 Apr 27;8(5):247. doi: 10.3390/nu8050247. Nutrients. 2016. PMID: 27128935 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Suppression of experimental arthritis through AMP-activated protein kinase activation and autophagy modulation.J Rheum Dis Treat. 2015 Feb 28;1(1):5. doi: 10.23937/2469-5726/1510005. J Rheum Dis Treat. 2015. PMID: 26120598 Free PMC article.
-
Non-cytotoxic doses of shikonin inhibit lipopolysaccharide-induced TNF-α expression via activation of the AMP-activated protein kinase signaling pathway.Exp Ther Med. 2020 Nov;20(5):45. doi: 10.3892/etm.2020.9173. Epub 2020 Sep 3. Exp Ther Med. 2020. PMID: 32952636 Free PMC article.
-
Intercellular interplay between Sirt1 signalling and cell metabolism in immune cell biology.Immunology. 2015 Aug;145(4):455-67. doi: 10.1111/imm.12473. Epub 2015 Jun 3. Immunology. 2015. PMID: 25890999 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Hotamisligil G. S. (2006) Nature 444, 860–867 - PubMed
-
- Yuan M., Konstantopoulos N., Lee J., Hansen L., Li Z. W., Karin M., Shoelson S. E. (2001) Science 293, 1673–1677 - PubMed
-
- Hirosumi J., Tuncman G., Chang L., Görgün C. Z., Uysal K. T., Maeda K., Karin M., Hotamisligil G. S. (2002) Nature 420, 333–336 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

