Successful computational prediction of novel imprinted genes from epigenomic features
- PMID: 20421412
- PMCID: PMC2897571
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.01355-09
Successful computational prediction of novel imprinted genes from epigenomic features
Abstract
Approximately 100 mouse genes undergo genomic imprinting, whereby one of the two parental alleles is epigenetically silenced. Imprinted genes influence processes including development, X chromosome inactivation, obesity, schizophrenia, and diabetes, motivating the identification of all imprinted loci. Local sequence features have been used to predict candidate imprinted genes, but rigorous testing using reciprocal crosses validated only three, one of which resided in previously identified imprinting clusters. Here we show that specific epigenetic features in mouse cells correlate with imprinting status in mice, and we identify hundreds of additional genes predicted to be imprinted in the mouse. We used a multitiered approach to validate imprinted expression, including use of a custom single nucleotide polymorphism array and traditional molecular methods. Of 65 candidates subjected to molecular assays for allele-specific expression, we found 10 novel imprinted genes that were maternally expressed in the placenta.
Figures
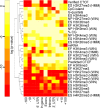
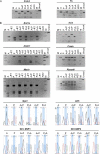
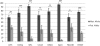
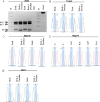
Similar articles
-
High-throughput analysis of candidate imprinted genes and allele-specific gene expression in the human term placenta.BMC Genet. 2010 Apr 19;11:25. doi: 10.1186/1471-2156-11-25. BMC Genet. 2010. PMID: 20403199 Free PMC article.
-
A survey for novel imprinted genes in the mouse placenta by mRNA-seq.Genetics. 2011 Sep;189(1):109-22. doi: 10.1534/genetics.111.130088. Epub 2011 Jul 29. Genetics. 2011. PMID: 21705755 Free PMC article.
-
A genome-wide approach reveals novel imprinted genes expressed in the human placenta.Epigenetics. 2012 Sep;7(9):1079-90. doi: 10.4161/epi.21495. Epub 2012 Aug 16. Epigenetics. 2012. PMID: 22894909 Free PMC article.
-
Imprinting of the mouse Igf2r gene depends on an intronic CpG island.Mol Cell Endocrinol. 1998 May 25;140(1-2):9-14. doi: 10.1016/s0303-7207(98)00022-7. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 1998. PMID: 9722161 Review.
-
Using next-generation RNA sequencing to identify imprinted genes.Heredity (Edinb). 2014 Aug;113(2):156-66. doi: 10.1038/hdy.2014.18. Epub 2014 Mar 12. Heredity (Edinb). 2014. PMID: 24619182 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Identification and Epigenetic Analysis of a Maternally Imprinted Gene Qpct.Mol Cells. 2015 Oct;38(10):859-65. doi: 10.14348/molcells.2015.0098. Epub 2015 Oct 12. Mol Cells. 2015. PMID: 26447138 Free PMC article.
-
Incorporating parent-of-origin effects in whole-genome prediction of complex traits.Genet Sel Evol. 2016 Apr 18;48:34. doi: 10.1186/s12711-016-0213-1. Genet Sel Evol. 2016. PMID: 27091137 Free PMC article.
-
A multiomic atlas of the aging hippocampus reveals molecular changes in response to environmental enrichment.Nat Commun. 2024 Jul 16;15(1):5829. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-49608-z. Nat Commun. 2024. PMID: 39013876 Free PMC article.
-
Identification and resolution of artifacts in the interpretation of imprinted gene expression.Brief Funct Genomics. 2010 Dec;9(5-6):374-84. doi: 10.1093/bfgp/elq020. Epub 2010 Sep 8. Brief Funct Genomics. 2010. PMID: 20829207 Free PMC article.
-
Conservation of Repeats at the Mammalian KCNQ1OT1-CDKN1C Region Suggests a Role in Genomic Imprinting.Evol Bioinform Online. 2017 Jun 16;13:1176934317715238. doi: 10.1177/1176934317715238. eCollection 2017. Evol Bioinform Online. 2017. PMID: 28659711 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Babak, T., B. Deveale, C. Armour, C. Raymond, M. A. Cleary, D. van der Kooy, J. M. Johnson, and L. P. Lim. 2008. Global survey of genomic imprinting by transcriptome sequencing. Curr. Biol. 18:1735-1741. - PubMed
-
- Bell, A. C., and G. Felsenfeld. 2000. Methylation of a CTCF-dependent boundary controls imprinted expression of the Igf2 gene. Nature 405:482-485. - PubMed
-
- Birger, Y., R. Shemer, J. Perk, and A. Razin. 1999. The imprinting box of the mouse Igf2r gene. Nature 397:84-88. - PubMed
-
- Boccaccio, I., H. Glatt-Deeley, F. Watrin, N. Roëckel, M. Lalande, and F. Muscatelli. 1999. The human MAGEL2 gene and its mouse homologue are paternally expressed and mapped to the Prader-Willi region. Hum. Mol. Genet. 8:2497-2505. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
