A two-tiered mechanism of EGFR inhibition by RALT/MIG6 via kinase suppression and receptor degradation
- PMID: 20421427
- PMCID: PMC2867293
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.201002032
A two-tiered mechanism of EGFR inhibition by RALT/MIG6 via kinase suppression and receptor degradation
Abstract
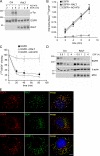
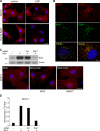
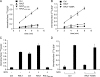
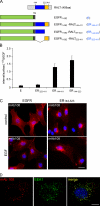
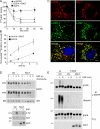
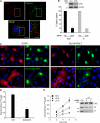
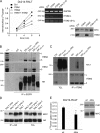
Signaling by epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) must be controlled tightly because aberrant EGFR activity may cause cell transformation. Receptor-associated late transducer (RALT) is a feedback inhibitor of EGFR whose genetic ablation in the mouse causes phenotypes due to EGFR-driven excess cell proliferation. RALT inhibits EGFR catalytic activation by docking onto EGFR kinase domain. We report here an additional mechanism of EGFR suppression mediated by RALT, demonstrating that RALT-bound EGF receptors undergo endocytosis and eventual degradation into lysosomes. Moreover, RALT rescues the endocytic deficit of EGFR mutants unable to undergo either endocytosis (Dc214) or degradation (Y1045F) and mediates endocytosis via a domain distinct from that responsible for EGFR catalytic suppression. Consistent with providing a scaffolding function for endocytic proteins, RALT drives EGFR endocytosis by binding to AP-2 and Intersectins. These data suggest a model in which binding of RALT to EGFR integrates suppression of EGFR kinase with receptor endocytosis and degradation, leading to durable repression of EGFR signaling.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The evolutionarily conserved EBR module of RALT/MIG6 mediates suppression of the EGFR catalytic activity.Oncogene. 2007 Dec 13;26(57):7833-46. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1210590. Epub 2007 Jun 18. Oncogene. 2007. PMID: 17599051
-
Differential parsing of EGFR endocytic flux among parallel internalization pathways in lung cancer cells with EGFR-activating mutations.Integr Biol (Camb). 2014 Mar;6(3):312-23. doi: 10.1039/c3ib40176f. Epub 2014 Jan 21. Integr Biol (Camb). 2014. PMID: 24445374
-
Regulation of EGFR trafficking and cell signaling by Sprouty2 and MIG6 in lung cancer cells.J Cell Sci. 2013 Oct 1;126(Pt 19):4339-48. doi: 10.1242/jcs.123208. Epub 2013 Jul 18. J Cell Sci. 2013. PMID: 23868981
-
Regulation of epidermal growth factor receptor signalling by inducible feedback inhibitors.J Cell Sci. 2011 Jun 1;124(Pt 11):1785-93. doi: 10.1242/jcs.083303. J Cell Sci. 2011. PMID: 21576352 Review.
-
Feedback inhibitors of the epidermal growth factor receptor signaling pathways.Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2009 Mar;41(3):511-5. doi: 10.1016/j.biocel.2008.06.019. Epub 2008 Aug 9. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2009. PMID: 18762271 Review.
Cited by
-
ErbB2 dephosphorylation and anti-proliferative effects of neuregulin-1 in ErbB2-overexpressing cells; re-evaluation of their low-affinity interaction.Sci Rep. 2013;3:1402. doi: 10.1038/srep01402. Sci Rep. 2013. PMID: 23466678 Free PMC article.
-
Pathways driving the endocytosis of mutant and wild-type EGFR in cancer.Oncoscience. 2014 Jul 29;1(8):504-12. doi: 10.18632/oncoscience.67. eCollection 2014. Oncoscience. 2014. PMID: 25594057 Free PMC article.
-
Loss of MIG6 Accelerates Initiation and Progression of Mutant Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor-Driven Lung Adenocarcinoma.Cancer Discov. 2015 May;5(5):534-49. doi: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-14-0750. Epub 2015 Mar 3. Cancer Discov. 2015. PMID: 25735773 Free PMC article.
-
High MIG-6 expression promotes tumor proliferation and metastasis of gastric cancer.J Cancer. 2025 Apr 21;16(8):2466-2475. doi: 10.7150/jca.98431. eCollection 2025. J Cancer. 2025. PMID: 40535815 Free PMC article.
-
Role of lysosomes in physiological activities, diseases, and therapy.J Hematol Oncol. 2021 May 14;14(1):79. doi: 10.1186/s13045-021-01087-1. J Hematol Oncol. 2021. PMID: 33990205 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Anastasi S., Sala G., Huiping C., Caprini E., Russo G., Iacovelli S., Lucini F., Ingvarsson S., Segatto O. 2005. Loss of RALT/MIG-6 expression in ERBB2-amplified breast carcinomas enhances ErbB-2 oncogenic potency and favors resistance to Herceptin. Oncogene. 24:4540–4548 10.1038/sj.onc.1208658 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

