Intensity-modulated chemoradiotherapy aiming to reduce dysphagia in patients with oropharyngeal cancer: clinical and functional results
- PMID: 20421546
- PMCID: PMC2881852
- DOI: 10.1200/JCO.2009.24.6199
Intensity-modulated chemoradiotherapy aiming to reduce dysphagia in patients with oropharyngeal cancer: clinical and functional results
Abstract
Purpose: To assess clinical and functional results of chemoradiotherapy for oropharyngeal cancer (OPC), utilizing intensity-modulated radiotherapy (IMRT) to spare the important swallowing structures to reduce post-therapy dysphagia.
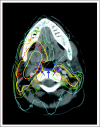
Patients and methods: This was a prospective study of weekly chemotherapy (carboplatin dosed at one times the area under the curve [AUC, AUC 1] and paclitaxel 30 mg/m(2)) concurrent with IMRT aiming to spare noninvolved parts of the swallowing structures: pharyngeal constrictors, glottic and supraglottic larynx, and esophagus as well as the oral cavity and major salivary glands. Swallowing was assessed by patient-reported Swallowing and Eating Domain scores, observer-rated scores, and videofluoroscopy (VF) before therapy and periodically after therapy through 2 years.
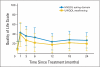
Results: Overall, 73 patients with stages III to IV OPC participated. At a median follow-up of 36 months, 3-year disease-free and locoregional recurrence-free survivals were 88% and 96%, respectively. All measures of dysphagia worsened soon after therapy; observer-rated and patient-reported scores recovered over time, but VF scores did not. At 1 year after therapy, observer-rated dysphagia was absent or minimal (scores 0 to 1) in all patients except four: one who was feeding-tube dependent and three who required soft diet. From pretherapy to 12 months post-therapy, the Swallowing and Eating Domain scores worsened on average (+/- standard deviation) by 10 +/- 21 and 13 +/- 19, respectively (on scales of 0 to 100), and VF scores (on scale of 1 to 7) worsened from 2.9 +/- 1.5 (mild dysphagia) to 4.1 +/- 0.9 (mild/moderate dysphagia).
Conclusion: Chemoradiotherapy with IMRT aiming to reduce dysphagia can be performed safely for OPC and has high locoregional tumor control rates. On average, long-term patient-reported, observer-rated, and objective measures of swallowing were only slightly worse than pretherapy measures, representing potential improvement compared with previous studies.
Conflict of interest statement
Authors' disclosures of potential conflicts of interest and author contributions are found at the end of this article.
Figures

References
-
- Rosenthal DI, Lewin JS, Eisbruch A. Prevention and treatment of dysphagia and aspiration after chemoradiation for head and neck cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2006;24:2636–2643. - PubMed
-
- Langendijk JA, Doornaert P, Verdonck-de Leeuw IM, et al. Impact of late treatment-related toxicity on quality of life among patients with head and neck cancer treated with radiotherapy. J Clin Oncol. 2008;26:3770–3776. - PubMed
-
- Eisbruch A, Schwartz M, Rasch C, et al. Dysphagia and aspiration after chemoradiotherapy for head-and-neck cancer: Which anatomic structures are affected and can they be spared by IMRT? Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2004;60:1425–1439. - PubMed
-
- Feng FY, Kim HM, Lyden TH, et al. Intensity-modulated radiotherapy of head and neck cancer aiming to reduce dysphagia: Early dose-effect relationships for the swallowing structures. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2007;68:1289–1298. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

