Phosphorylation-regulated binding of Ctp1 to Nbs1 is critical for repair of DNA double-strand breaks
- PMID: 20421724
- PMCID: PMC3154839
- DOI: 10.4161/cc.9.8.11260
Phosphorylation-regulated binding of Ctp1 to Nbs1 is critical for repair of DNA double-strand breaks
Abstract
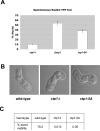
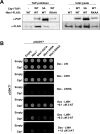
Repair of DNA double-strand breaks (DSBs) is critical for cell survival and for maintaining genome stability in eukaryotes. In Schizosaccharomyces pombe, the Mre11-Rad50-Nbs1 (MRN) complex and Ctp1 cooperate to perform the initial steps that process and repair these DNA lesions via homologous recombination (HR). While Ctp1 is recruited to DSBs in an MRN-dependent manner, the specific mechanism of this process remained unclear. We recently found that Ctp1 is phosphorylated on a domain rich in putative Casein kinase 2 (CK2) phosphoacceptor sites that resembles the SDTD repeats of Mdc1. Furthermore, phosphorylation of this motif is required for interaction with the FHA domain of Nbs1 that localizes Ctp1 to DSB sites. Here, we review and discuss these findings, and we present new data that further characterize the cellular consequences of mutating CK2 phosphorylation motifs of Ctp1, including data showing that these sites are critical for meiosis.
Figures

References
-
- Williams RS, Williams JS, Tainer JA. Mre11-Rad50-Nbs1 is a keystone complex connecting DNA repair machinery, double-strand break signaling, and the chromatin template. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2007;85:509–20. - PubMed
-
- Durocher D, Henckel J, Fersht AR, Jackson SP. The FHA domain is a modular phosphopeptide recognition motif. Mol Cell. 1999;4:387–94. - PubMed
-
- Yu X, Chini CC, He M, Mer G, Chen J. The BRCT domain is a phospho-protein binding domain. Science. 2003;302:639–42. - PubMed
-
- Kobayashi J, Tauchi H, Sakamoto S, Nakamura A, Morishima K, Matsuura S, et al. NBS1 localizes to gamma-H2AX foci through interaction with the FHA/BRCT domain. Curr Biol. 2002;12:1846–51. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
