Individual microRNAs (miRNAs) display distinct mRNA targeting "rules"
- PMID: 20421741
- PMCID: PMC3040646
- DOI: 10.4161/rna.7.3.11693
Individual microRNAs (miRNAs) display distinct mRNA targeting "rules"
Abstract
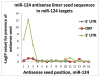
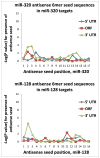
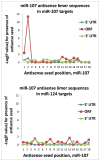
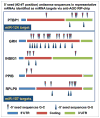
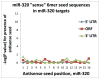
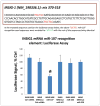
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) guide Argonaute (AGO)-containing microribonucleoprotein (miRNP) complexes to target mRNAs.It has been assumed that miRNAs behave similarly to each other with regard to mRNA target recognition. The usual assumptions, which are based on prior studies, are that miRNAs target preferentially sequences in the 3'UTR of mRNAs,guided by the 5' "seed" portion of the miRNAs. Here we isolated AGO- and miRNA-containing miRNPs from human H4 tumor cells by co-immunoprecipitation (co-IP) with anti-AGO antibody. Cells were transfected with miR-107, miR-124,miR-128, miR-320, or a negative control miRNA. Co-IPed RNAs were subjected to downstream high-density Affymetrix Human Gene 1.0 ST microarray analyses using an assay we validated previously-a "RIP-Chip" experimental design. RIP-Chip data provided a list of mRNAs recruited into the AGO-miRNP in correlation to each miRNA. These experimentally identified miRNA targets were analyzed for complementary six nucleotide "seed" sequences within the transfected miRNAs. We found that miR-124 targets tended to have sequences in the 3'UTR that would be recognized by the 5' seed of miR-124, as described in previous studies. By contrast, miR-107 targets tended to have 'seed' sequences in the mRNA open reading frame, but not the 3' UTR. Further, mRNA targets of miR-128 and miR-320 are less enriched for 6-mer seed sequences in comparison to miR-107 and miR-124. In sum, our data support the importance of the 5' seed in determining binding characteristics for some miRNAs; however, the "binding rules" are complex, and individual miRNAs can have distinct sequence determinants that lead to mRNA targeting.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Anti-Argonaute RIP-Chip shows that miRNA transfections alter global patterns of mRNA recruitment to microribonucleoprotein complexes.RNA. 2010 Feb;16(2):394-404. doi: 10.1261/rna.1905910. Epub 2009 Dec 30. RNA. 2010. PMID: 20042474 Free PMC article.
-
Specific sequence determinants of miR-15/107 microRNA gene group targets.Nucleic Acids Res. 2011 Oct;39(18):8163-72. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkr532. Epub 2011 Jun 30. Nucleic Acids Res. 2011. PMID: 21724616 Free PMC article.
-
Binding sites of miR-1273 family on the mRNA of target genes.Biomed Res Int. 2014;2014:620530. doi: 10.1155/2014/620530. Epub 2014 Aug 26. Biomed Res Int. 2014. PMID: 25243165 Free PMC article.
-
The Non-Canonical Aspects of MicroRNAs: Many Roads to Gene Regulation.Cells. 2019 Nov 19;8(11):1465. doi: 10.3390/cells8111465. Cells. 2019. PMID: 31752361 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Experimental strategies for microRNA target identification.Nucleic Acids Res. 2011 Sep 1;39(16):6845-53. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkr330. Epub 2011 Jun 7. Nucleic Acids Res. 2011. PMID: 21652644 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Novel human ABCC9/SUR2 brain-expressed transcripts and an eQTL relevant to hippocampal sclerosis of aging.J Neurochem. 2015 Sep;134(6):1026-39. doi: 10.1111/jnc.13202. Epub 2015 Jul 15. J Neurochem. 2015. PMID: 26115089 Free PMC article.
-
Principles of miRNA-target regulation in metazoan models.Int J Mol Sci. 2013 Aug 7;14(8):16280-302. doi: 10.3390/ijms140816280. Int J Mol Sci. 2013. PMID: 23965954 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mixed-species biofilm compromises wound healing by disrupting epidermal barrier function.J Pathol. 2014 Aug;233(4):331-343. doi: 10.1002/path.4360. Epub 2014 May 27. J Pathol. 2014. PMID: 24771509 Free PMC article.
-
Circulating microRNAs as biomarkers, therapeutic targets, and signaling molecules.Sensors (Basel). 2012;12(3):3359-69. doi: 10.3390/s120303359. Epub 2012 Mar 8. Sensors (Basel). 2012. PMID: 22737013 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Small RNA-mediated regulation of iPS cell generation.EMBO J. 2011 Mar 2;30(5):823-34. doi: 10.1038/emboj.2011.2. Epub 2011 Feb 1. EMBO J. 2011. PMID: 21285944 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ambros V. The functions of animal microRNAs. Nature. 2004;431:350–5. - PubMed
-
- Wang W, Nelson PT, Tang G. WILEY ENCYCLOPEDIA OF CHEMICAL BIOLOGY. John Wiley & Sons, Inc; 2008. RNA Interference, Mechanisms and Proteins Involved.
-
- Orom UA, Lund AH. Experimental identification of microRNA targets. Gene. 2009 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
