Early identification of risk factors for sudden cardiac death
- PMID: 20421887
- PMCID: PMC3052394
- DOI: 10.1038/nrcardio.2010.52
Early identification of risk factors for sudden cardiac death
Abstract
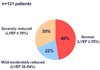
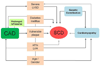
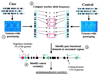
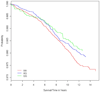
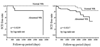
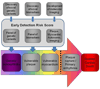
Sudden cardiac death (SCD) is a global health issue. The unexpected nature of this devastating condition compounds the urgency of discovering methods for early detection of risk, which will lead to more effective prevention. However, the complex and dynamic nature of SCD continues to present a considerable challenge for the early identification of risk factors. Measurement of the left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) is currently the only major risk factor used for stratification in clinical practice. Severely decreased LVEF is likely to manifest late in the natural history of SCD, however, and may only affect a small subgroup of patients who will suffer SCD. A growing body of literature describes novel risk markers and predictors of SCD, such as high-risk phenotypes, genetic variants and biomarkers. This Review will discuss the potential utility of these markers as early identifiers of risk, and suggests a framework for the conduct of future studies for the discovery, validation, and deployment of novel SCD risk factors.
Figures

References
-
- Chugh SS, et al. Current burden of sudden cardiac death: multiple source surveillance versus retrospective death certificate-based review in a large U.S. community. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2004;44:1268–1275. - PubMed
-
- Zipes DP, Wellens HJ. Sudden cardiac death. Circulation. 1998;98:2334–2351. - PubMed
-
- Huikuri H, Castellanos A, Myerburg R. Sudden death due to cardiac arrhythmias. New England Journal of …. 2001 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

