Clinical reasoning in the real world is mediated by bounded rationality: implications for diagnostic clinical practice guidelines
- PMID: 20421920
- PMCID: PMC2857648
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0010265
Clinical reasoning in the real world is mediated by bounded rationality: implications for diagnostic clinical practice guidelines
Abstract
Background: Little is known about the reasoning mechanisms used by physicians in decision-making and how this compares to diagnostic clinical practice guidelines. We explored the clinical reasoning process in a real life environment.
Method: This is a qualitative study evaluating transcriptions of sixteen physicians' reasoning during appointments with patients, clinical discussions between specialists, and personal interviews with physicians affiliated to a hospital in Brazil.
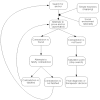
Results: FOUR MAIN THEMES WERE IDENTIFIED: simple and robust heuristics, extensive use of social environment rationality, attempts to prove diagnostic and therapeutic hypothesis while refuting potential contradictions using positive test strategy, and reaching the saturation point. Physicians constantly attempted to prove their initial hypothesis while trying to refute any contradictions. While social environment rationality was the main factor in the determination of all steps of the clinical reasoning process, factors such as referral letters and number of contradictions associated with the initial hypothesis had influence on physicians' confidence and determination of the threshold to reach a final decision.
Discussion: Physicians rely on simple heuristics associated with environmental factors. This model allows for robustness, simplicity, and cognitive energy saving. Since this model does not fit into current diagnostic clinical practice guidelines, we make some propositions to help its integration.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Reasoning, decision making and rationality.Cognition. 1993 Oct-Nov;49(1-2):165-87. doi: 10.1016/0010-0277(93)90039-x. Cognition. 1993. PMID: 8287673 Review.
-
Studies in Ecological Rationality.Top Cogn Sci. 2022 Jul;14(3):467-491. doi: 10.1111/tops.12567. Epub 2021 Jul 26. Top Cogn Sci. 2022. PMID: 34310848
-
When is rational to order a diagnostic test, or prescribe treatment: the threshold model as an explanation of practice variation.Eur J Clin Invest. 2015 May;45(5):485-93. doi: 10.1111/eci.12421. Epub 2015 Mar 9. Eur J Clin Invest. 2015. PMID: 25675907 Review.
-
[The analysis of physicians' work: announcing the end of attempts at in vitro fertilization].Encephale. 2003 Jul-Aug;29(4 Pt 1):293-305. Encephale. 2003. PMID: 14615699 French.
-
Approach to making the availability heuristic less available.BMJ Qual Saf. 2020 Jul;29(7):528-530. doi: 10.1136/bmjqs-2020-010831. Epub 2020 Jan 20. BMJ Qual Saf. 2020. PMID: 31959715 No abstract available.
Cited by
-
Evidence in clinical reasoning: a computational linguistics analysis of 789,712 medical case summaries 1983-2012.BMC Med Inform Decis Mak. 2015 Mar 21;15:19. doi: 10.1186/s12911-015-0136-8. BMC Med Inform Decis Mak. 2015. PMID: 25880840 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical reasoning in traditional medicine exemplified by the clinical encounter of Korean medicine: a narrative review.Integr Med Res. 2021 Jun;10(2):100641. doi: 10.1016/j.imr.2020.100641. Epub 2020 Aug 11. Integr Med Res. 2021. PMID: 33384923 Free PMC article. Review.
-
What's new in critical illness and injury science? Preventing surgical infections requires the right antibiotic for the right duration.Int J Crit Illn Inj Sci. 2012 May;2(2):55-6. doi: 10.4103/2229-5151.97267. Int J Crit Illn Inj Sci. 2012. PMID: 22837891 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
'My first thoughts are…': a Framework Method analysis of UK general practice healthcare professionals' internal dialogue and clinical reasoning processes when seeing patients living with obesity in primary care.BMJ Open. 2025 Apr 2;15(4):e086722. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2024-086722. BMJ Open. 2025. PMID: 40180408 Free PMC article.
-
Exploration of rural physicians' lived experience of practising outside their usual scope of practice to provide access to essential medical care (clinical courage): an international phenomenological study.BMJ Open. 2020 Aug 26;10(8):e037705. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2020-037705. BMJ Open. 2020. PMID: 32847915 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Berner ES, Graber ML. Overconfidence as a cause of diagnostic error in medicine. 23Am J Med. 2008;121(5 Suppl) - PubMed
-
- Woolf SH. An organized analytic framework for practice guideline development: using the analytic logic as a guide for reviewing evidence, developing recommendations, and explaining the results. In: McCormick KA, Moore SR, Siegel RA, editors. Clinical Practice Guideline Development: Methodology Perspectives. AHCPR Pub No 95-0009. Rockville, Md: Agency for Health Care Policy and Research; 1995. pp. 105–113.
-
- Saver BG, Taylor TR, Woods NF, Stevens NG. Physician policies on the use of preventive hormone therapy. Am J Prev Med. 1997;13:358–365. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources