Two coregulated efflux transporters modulate intracellular heme and protoporphyrin IX availability in Streptococcus agalactiae
- PMID: 20421944
- PMCID: PMC2858704
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1000860
Two coregulated efflux transporters modulate intracellular heme and protoporphyrin IX availability in Streptococcus agalactiae
Abstract
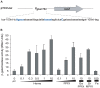
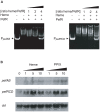
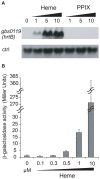
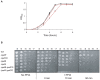
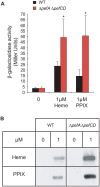
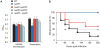
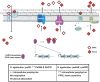
Streptococcus agalactiae is a major neonatal pathogen whose infectious route involves septicemia. This pathogen does not synthesize heme, but scavenges it from blood to activate a respiration metabolism, which increases bacterial cell density and is required for full virulence. Factors that regulate heme pools in S. agalactiae are unknown. Here we report that one main strategy of heme and protoporphyrin IX (PPIX) homeostasis in S. agalactiae is based on a regulated system of efflux using two newly characterized operons, gbs1753 gbs1752 (called pefA pefB), and gbs1402 gbs1401 gbs1400 (called pefR pefC pefD), where pef stands for 'porphyrin-regulated efflux'. In vitro and in vivo data show that PefR, a MarR-superfamily protein, is a repressor of both operons. Heme or PPIX both alleviate PefR-mediated repression. We show that bacteria inactivated for both Pef efflux systems display accrued sensitivity to these porphyrins, and give evidence that they accumulate intracellularly. The DeltapefR mutant, in which both pef operons are up-regulated, is defective for heme-dependent respiration, and attenuated for virulence. We conclude that this new efflux regulon controls intracellular heme and PPIX availability in S. agalactiae, and is needed for its capacity to undergo respiration metabolism, and to infect the host.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Protoporphyrin (PPIX) efflux by the MacAB-TolC pump in Escherichia coli.Microbiologyopen. 2014 Dec;3(6):849-59. doi: 10.1002/mbo3.203. Epub 2014 Sep 26. Microbiologyopen. 2014. PMID: 25257218 Free PMC article.
-
Visualization of the role of host heme on the virulence of the heme auxotroph Streptococcus agalactiae.Sci Rep. 2017 Jan 16;7:40435. doi: 10.1038/srep40435. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 28091535 Free PMC article.
-
Roles of environmental heme, and menaquinone, in streptococcus agalactiae.Biometals. 2006 Apr;19(2):205-10. doi: 10.1007/s10534-005-5419-6. Biometals. 2006. PMID: 16718605 Review.
-
Cellular Management of Zinc in Group B Streptococcus Supports Bacterial Resistance against Metal Intoxication and Promotes Disseminated Infection.mSphere. 2021 May 19;6(3):e00105-21. doi: 10.1128/mSphere.00105-21. mSphere. 2021. PMID: 34011683 Free PMC article.
-
Surface proteins of Streptococcus agalactiae and related proteins in other bacterial pathogens.Clin Microbiol Rev. 2005 Jan;18(1):102-27. doi: 10.1128/CMR.18.1.102-127.2005. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2005. PMID: 15653821 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Genome sequence of a food spoilage lactic acid bacterium, Leuconostoc gasicomitatum LMG 18811T, in association with specific spoilage reactions.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2011 Jul;77(13):4344-51. doi: 10.1128/AEM.00102-11. Epub 2011 May 13. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2011. PMID: 21571876 Free PMC article.
-
Protoporphyrin (PPIX) efflux by the MacAB-TolC pump in Escherichia coli.Microbiologyopen. 2014 Dec;3(6):849-59. doi: 10.1002/mbo3.203. Epub 2014 Sep 26. Microbiologyopen. 2014. PMID: 25257218 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization and expression analysis of the transferrin gene in Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) and its upregulation in response to Streptococcus agalactiae infection.Fish Physiol Biochem. 2014 Oct;40(5):1473-85. doi: 10.1007/s10695-014-9941-8. Epub 2014 Apr 26. Fish Physiol Biochem. 2014. PMID: 24770882
-
A sensitive bacterial-growth-based test reveals how intestinal Bacteroides meet their porphyrin requirement.BMC Microbiol. 2015 Dec 29;15:282. doi: 10.1186/s12866-015-0616-0. BMC Microbiol. 2015. PMID: 26715069 Free PMC article.
-
FapR regulates HssRS-mediated heme homeostasis in Bacillus anthracis.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Jul 8:2024.07.08.602573. doi: 10.1101/2024.07.08.602573. bioRxiv. 2024. Update in: mBio. 2025 Jun 11;16(6):e0205724. doi: 10.1128/mbio.02057-24. PMID: 39026866 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
-
- Mense SM, Zhang L. Heme: a versatile signaling molecule controlling the activities of diverse regulators ranging from transcription factors to MAP kinases. Cell Res. 2006;16:681–692. - PubMed
-
- Shepherd M, Heath MD, Poole RK. NikA binds heme: a new role for an Escherichia coli periplasmic nickel-binding protein. Biochemistry. 2007;46:5030–5037. - PubMed
-
- Gilles-Gonzalez MA, Gonzalez G. Signal transduction by heme-containing PAS-domain proteins. J Appl Physiol. 2004;96:774–783. - PubMed
-
- Kumar S, Bandyopadhyay U. Free heme toxicity and its detoxification systems in human. Toxicol Lett. 2005;157:175–188. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

