Novel riboswitch ligand analogs as selective inhibitors of guanine-related metabolic pathways
- PMID: 20421948
- PMCID: PMC2858708
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1000865
Novel riboswitch ligand analogs as selective inhibitors of guanine-related metabolic pathways
Abstract
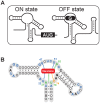
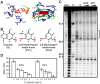
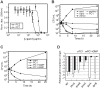
Riboswitches are regulatory elements modulating gene expression in response to specific metabolite binding. It has been recently reported that riboswitch agonists may exhibit antimicrobial properties by binding to the riboswitch domain. Guanine riboswitches are involved in the regulation of transport and biosynthesis of purine metabolites, which are critical for the nucleotides cellular pool. Upon guanine binding, these riboswitches stabilize a 5'-untranslated mRNA structure that causes transcription attenuation of the downstream open reading frame. In principle, any agonistic compound targeting a guanine riboswitch could cause gene repression even when the cell is starved for guanine. Antibiotics binding to riboswitches provide novel antimicrobial compounds that can be rationally designed from riboswitch crystal structures. Using this, we have identified a pyrimidine compound (PC1) binding guanine riboswitches that shows bactericidal activity against a subgroup of bacterial species including well-known nosocomial pathogens. This selective bacterial killing is only achieved when guaA, a gene coding for a GMP synthetase, is under the control of the riboswitch. Among the bacterial strains tested, several clinical strains exhibiting multiple drug resistance were inhibited suggesting that PC1 targets a different metabolic pathway. As a proof of principle, we have used a mouse model to show a direct correlation between the administration of PC1 and the reduction of Staphylococcus aureus infection in mammary glands. This work establishes the possibility of using existing structural knowledge to design novel guanine riboswitch-targeting antibiotics as powerful and selective antimicrobial compounds. Particularly, the finding of this new guanine riboswitch target is crucial as community-acquired bacterial infections have recently started to emerge.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures

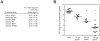

Similar articles
-
Experimental treatment of Staphylococcus aureus bovine intramammary infection using a guanine riboswitch ligand analog.J Dairy Sci. 2013 Feb;96(2):1000-8. doi: 10.3168/jds.2012-5890. Epub 2012 Dec 14. J Dairy Sci. 2013. PMID: 23245959
-
De Novo Guanine Biosynthesis but Not the Riboswitch-Regulated Purine Salvage Pathway Is Required for Staphylococcus aureus Infection In Vivo.J Bacteriol. 2016 Jun 27;198(14):2001-2015. doi: 10.1128/JB.00051-16. Print 2016 Jul 15. J Bacteriol. 2016. PMID: 27161118 Free PMC article.
-
Inactivation of the riboswitch-controlled GMP synthase GuaA in Clostridioides difficile is associated with severe growth defects and poor infectivity in a mouse model of infection.RNA Biol. 2021 Nov 12;18(sup2):699-710. doi: 10.1080/15476286.2021.1978768. Epub 2021 Oct 6. RNA Biol. 2021. PMID: 34612173 Free PMC article.
-
Riboswitches: discovery of drugs that target bacterial gene-regulatory RNAs.Acc Chem Res. 2011 Dec 20;44(12):1329-38. doi: 10.1021/ar200039b. Epub 2011 May 26. Acc Chem Res. 2011. PMID: 21615107 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[Novel targets for antibiotics discovery: riboswitches].Yao Xue Xue Bao. 2013 Sep;48(9):1361-8. Yao Xue Xue Bao. 2013. PMID: 24358767 Review. Chinese.
Cited by
-
X-Ray Crystallography to Study Conformational Changes in a TPP Riboswitch.Methods Mol Biol. 2023;2568:213-232. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-2687-0_14. Methods Mol Biol. 2023. PMID: 36227571
-
Thiamin (vitamin B1) biosynthesis and regulation: a rich source of antimicrobial drug targets?Int J Biol Sci. 2011 Jan 9;7(1):41-52. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.7.41. Int J Biol Sci. 2011. PMID: 21234302 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Constitutive regulatory activity of an evolutionarily excluded riboswitch variant.J Biol Chem. 2011 Aug 5;286(31):27406-15. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M111.229047. Epub 2011 Jun 15. J Biol Chem. 2011. PMID: 21676871 Free PMC article.
-
The current riboswitch landscape in Clostridioides difficile.Microbiology (Reading). 2024 Oct;170(10):001508. doi: 10.1099/mic.0.001508. Microbiology (Reading). 2024. PMID: 39405103 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Term-seq reveals abundant ribo-regulation of antibiotics resistance in bacteria.Science. 2016 Apr 8;352(6282):aad9822. doi: 10.1126/science.aad9822. Science. 2016. PMID: 27120414 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Blount KF, Breaker RR. Riboswitches as antibacterial drug targets. Nat Biotechnol. 2006;24:1558–1564. - PubMed
-
- Talbot GH, Bradley J, Edwards JE, Jr, Gilbert D, Scheld M, et al. Bad bugs need drugs: an update on the development pipeline from the Antimicrobial Availability Task Force of the Infectious Diseases Society of America. Clin Infect Dis. 2006;42:657–668. - PubMed
-
- Popovich KJ, Hota B, Weinstein RA. Treatment of community-associated methicillin-resistant staphylococcus aureus. Curr Infect Dis Rep. 2008;10:411–420. - PubMed
-
- Pofelski J, Pavese P, Brion JP, Marrakchi C, Gay E, et al. Staphylococcus aureus meningitis with intermediate sensitivity to glycopeptides. Therapeutic indications. Presse Med. 2003;32:217–220. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

