Drosophila SAF-B links the nuclear matrix, chromosomes, and transcriptional activity
- PMID: 20422039
- PMCID: PMC2857882
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0010248
Drosophila SAF-B links the nuclear matrix, chromosomes, and transcriptional activity
Abstract
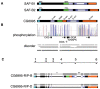
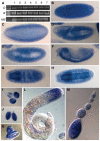
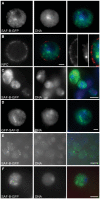
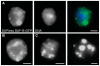
Induction of gene expression is correlated with alterations in nuclear organization, including proximity to other active genes, to the nuclear cortex, and to cytologically distinct domains of the nucleus. Chromosomes are tethered to the insoluble nuclear scaffold/matrix through interaction with Scaffold/Matrix Attachment Region (SAR/MAR) binding proteins. Identification and characterization of proteins involved in establishing or maintaining chromosome-scaffold interactions is necessary to understand how the nucleus is organized and how dynamic changes in attachment are correlated with alterations in gene expression. We identified and characterized one such scaffold attachment factor, a Drosophila homolog of mammalian SAF-B. The large nuclei and chromosomes of Drosophila have allowed us to show that SAF-B inhabits distinct subnuclear compartments, forms weblike continua in nuclei of salivary glands, and interacts with discrete chromosomal loci in interphase nuclei. These interactions appear mediated either by DNA-protein interactions, or through RNA-protein interactions that can be altered during changes in gene expression programs. Extraction of soluble nuclear proteins and DNA leaves SAF-B intact, showing that this scaffold/matrix-attachment protein is a durable component of the nuclear matrix. Together, we have shown that SAF-B links the nuclear scaffold, chromosomes, and transcriptional activity.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Nuclear organization by satellite DNA, SAF-A/hnRNPU and matrix attachment regions.Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2022 Aug;128:61-68. doi: 10.1016/j.semcdb.2022.04.018. Epub 2022 Apr 25. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2022. PMID: 35484025 Review.
-
[Trithorax protein, a global factor for maintenance of tissue specific gene activation in Drosophila melanogaster, is associated with the nuclear matrix].Genetika. 2003 Feb;39(2):250-8. Genetika. 2003. PMID: 12669422 Russian.
-
Scaffold attachment factor A (SAF-A) is concentrated in inactive X chromosome territories through its RGG domain.Chromosoma. 2003 Dec;112(4):173-82. doi: 10.1007/s00412-003-0258-0. Epub 2003 Nov 8. Chromosoma. 2003. PMID: 14608463
-
Tamoxifen-bound estrogen receptor (ER) strongly interacts with the nuclear matrix protein HET/SAF-B, a novel inhibitor of ER-mediated transactivation.Mol Endocrinol. 2000 Mar;14(3):369-81. doi: 10.1210/mend.14.3.0432. Mol Endocrinol. 2000. PMID: 10707955
-
Revisiting the function of nuclear scaffold/matrix binding proteins in X chromosome inactivation.RNA Biol. 2011 Sep-Oct;8(5):735-9. doi: 10.4161/rna.8.5.16367. Epub 2011 Sep 1. RNA Biol. 2011. PMID: 21881412 Review.
Cited by
-
Beyond cell-cell adhesion: Emerging roles of the tight junction scaffold ZO-2.Tissue Barriers. 2013 Apr 1;1(2):e25039. doi: 10.4161/tisb.25039. Tissue Barriers. 2013. PMID: 24665396 Free PMC article. Review.
-
In vivo mapping of arabidopsis scaffold/matrix attachment regions reveals link to nucleosome-disfavoring poly(dA:dT) tracts.Plant Cell. 2014 Jan;26(1):102-20. doi: 10.1105/tpc.113.121194. Epub 2014 Jan 31. Plant Cell. 2014. PMID: 24488963 Free PMC article.
-
FUS interacts with nuclear matrix-associated protein SAFB1 as well as Matrin3 to regulate splicing and ligand-mediated transcription.Sci Rep. 2016 Oct 12;6:35195. doi: 10.1038/srep35195. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 27731383 Free PMC article.
-
Nuclear architecture and the structural basis of mitotic memory.Chromosome Res. 2023 Feb 2;31(1):8. doi: 10.1007/s10577-023-09714-y. Chromosome Res. 2023. PMID: 36725757 Review.
-
Scaffold attachment factor B suppresses HIV-1 infection of CD4+ T cells by preventing binding of RNA polymerase II to HIV-1's long terminal repeat.J Biol Chem. 2018 Aug 3;293(31):12177-12185. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA118.002018. Epub 2018 Jun 10. J Biol Chem. 2018. PMID: 29887524 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Sutherland H, Bickmore WA. Transcription factories: gene expression in unions? Nat Rev Genet. 2009;10:457–466. - PubMed
-
- Solovei I, Cavallo A, Schermelleh L, Jaunin F, Scasselati C, et al. Spatial preservation of nuclear chromatin architecture during three-dimensional fluorescence in situ hybridization (3D-FISH). Exp Cell Res. 2002;276:10–23. - PubMed
-
- Berger AB, Cabal GG, Fabre E, Duong T, Buc H, et al. High-resolution statistical mapping reveals gene territories in live yeast. Nat Methods. 2008;5:1031–1037. - PubMed
-
- Clegg NJ, Honda BM, Whitehead IP, Grigliatti TA, Wakimoto B, et al. Suppressors of position-effect variegation in Drosophila melanogaster affect expression of the heterochromatic gene light in the absence of a chromosome rearrangement. Genome. 1998;41:495–503. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

