Piperacillin-associated pulmonary infiltrates with eosinophilia: a case report
- PMID: 20422064
- PMCID: PMC2866217
- DOI: 10.1155/2010/670153
Piperacillin-associated pulmonary infiltrates with eosinophilia: a case report
Abstract
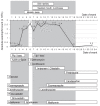
A case of pulmonary infiltrates with eosinophilia attributed to piperacillin tazobactam therapy is described. A 54-year-old woman was treated for a suspected severe urinary tract infection with piperacillin tazobactam. Four days later, she developed fever, chills, shortness of breath and intermittent chest pains. Eosinophilia was noted in peripheral blood and, subsequently, on bronchoalveolar lavage. Transbronchial biopsy showed tissue infiltrates with eosinophilia. No evidence of bacterial, fungal and parasitic infection, or vasculitis was observed. Her symptoms and peripheral eosinophilia subsided after drug discontinuation and oral prednisone treatment. Piperacillin is an extended-spectrum penicillin antibiotic prescribed for moderate to severe infections. The common adverse reactions to piperacillin include nausea, vomiting, diarrhea and rash. Pulmonary infiltrates with eosinophilia is a rare adverse reaction, but one that may result in significant morbidity. Physicians should be aware of this rare but important adverse reaction to piperacillin.
Les auteurs décrivent un cas d’infiltrats pulmonaires à éosinophiles attribués à une thérapie à la pipéracilline et au tazobactam. Une femme de 54 ans ayant une grave infection urinaire présumée a reçu un traitement à la pipéracilline et au tazobactam. Quatre jours plus tard, elle s’est mise à faire de la fièvre, à avoir des frissons, à être essoufflée et à souffrir de douleurs thoraciques intermittentes. On a constaté la présence d’éosinophiles dans le sang périphérique et, par la suite, dans le lavage bronchoalvéolaire. La biopsie transbronchique a révélé la présence d’infiltrats tissulaires à éosinophiles. On n’a observé aucuns signes d’infection bactérienne, fongique ou parasitaire ou de vasculite. Les symptômes et l’éosinophilie périphérique se sont résorbés après l’arrêt de la pharmacothérapie et un traitement à la prednisone par voie orale. La pipéracilline est un antibiotique à large spectre du groupe de la pénicilline, prescrit en cas d’infections modérées à graves. Les effets indésirables courants de la pipéracilline sont les nausées, les vomissements, la diarrhée et les éruptions. Les infiltrats pulmonaires à éosinophiles sont une réaction indésirable rare qui peut entraîner une importante morbidité. Les médecins devraient connaître cet effet indésirable à la pipéracilline, car il est rare mais grave
Figures
Similar articles
-
An unusual case of piperacillin-tazobactam-induced fever, eosinophilia, thrombocytopenia and liver damage.Eur J Hosp Pharm. 2022 Mar;29(e1):e91-e94. doi: 10.1136/ejhpharm-2020-002575. Epub 2021 Feb 8. Eur J Hosp Pharm. 2022. PMID: 33558219 Free PMC article.
-
Eosinophilic pneumonia presenting as life-threatening ARDS.BMJ Case Rep. 2015 Jul 6;2015:bcr2014207379. doi: 10.1136/bcr-2014-207379. BMJ Case Rep. 2015. PMID: 26150613 Free PMC article.
-
Drug reaction with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms (DRESS) syndrome in two young children: the importance of an early diagnosis.Ital J Pediatr. 2018 Aug 15;44(1):93. doi: 10.1186/s13052-018-0535-4. Ital J Pediatr. 2018. PMID: 30111350 Free PMC article.
-
Antibiotic-induced black hairy tongue: two case reports and a review of the literature.J Int Med Res. 2020 Oct;48(10):300060520961279. doi: 10.1177/0300060520961279. J Int Med Res. 2020. PMID: 33044871 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[Piperacillin/tazobactam--Tazocin. A penicillin-based alternative to 3rd generation cephalosporins and carbapenems].Ugeskr Laeger. 2002 May 13;164(20):2606-10. Ugeskr Laeger. 2002. PMID: 12043402 Review. Danish.
Cited by
-
Chronic eosinophilic pneumonia due to radiographic contrast administration: an orphan disease?Drug Des Devel Ther. 2012;6:385-9. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S37937. Epub 2012 Dec 10. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2012. PMID: 23251088 Free PMC article.
-
Undetected Causes of Death in Hospitalized Elderly with COVID-19: Lessons from Autopsy.J Clin Med. 2021 Mar 24;10(7):1337. doi: 10.3390/jcm10071337. J Clin Med. 2021. PMID: 33804890 Free PMC article.
-
A combination of predispositions and exposures as responsible for acute eosinophilic pneumonia.Multidiscip Respir Med. 2014 Jan 30;9(1):7. doi: 10.1186/2049-6958-9-7. Multidiscip Respir Med. 2014. PMID: 24475879 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Tefferi A. Blood eosinophilia: A new paradigm in disease classification, diagnosis, and treatment. Mayo Clin Proc. 2005;80:75–83. - PubMed
-
- Allen JN, Davis WB. Eosinophilic lung diseases. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1994;150(5Pt1):1423–38. - PubMed
-
- Ibrahim AS, Ghadban WK, Arrayes M.Eosinophilic pleural effusion due to cloxacillin and piperacillin/tazobactum<http://www.hmc.org.qa/qmj/qmj2006/JUNE2006/case/case2.htm> (Accessed July 2009).
-
- Nakamura T, Kawanami Y, Yoshimoto M, et al. [Case of severe eosinophilic pneumonia, induced by several antibiotics, requiring mechanical ventilation] Nihon Kokyuki Gakkai Zasshi. 2006;44:695–700. - PubMed
-
- Yamamoto T, Tanida T, Ueta E, et al. Pulmonary infiltration with eosinophilia (PIE) syndrome induced by antibiotics, PIPC and TFLX during cancer treatment. Oral Oncol. 2001;37:471–5. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical