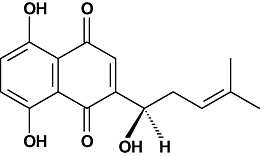
Shikonin reduces oedema induced by phorbol ester by interfering with IkappaBalpha degradation thus inhibiting translocation of NF-kappaB to the nucleus
- PMID: 20423347
- PMCID: PMC2874859
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.2010.00696.x
Shikonin reduces oedema induced by phorbol ester by interfering with IkappaBalpha degradation thus inhibiting translocation of NF-kappaB to the nucleus
Abstract
Background and purpose: In the present paper we studied the effect of shikonin on ear oedema induced by 12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol-13-acetate (TPA), and determined the mechanisms through which shikonin might exert its topical anti-inflammatory action.
Experimental approach: Acute ear oedema was induced in mice by topical application of TPA. The in vitro assays used macrophages RAW 264.7 cells stimulated with lipopolysaccharide. Cyclooxygenase-2, inducible nitric oxide synthase, protein kinase Calpha, extracellular signal-regulated protein kinase (ERK), phosphorylated ERK (pERK), c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK), pJNK, p38, p-p38, p65, p-p65, inhibitor protein of nuclear factor-kappaB (NF-kappaB) (IkappaBalpha) and pIkappaBalpha were measured by Western blotting, activation and binding of NF-kappaB to DNA was detected by reporter gene and electrophoretic mobility shift assay, respectively, and NF-kappaB p65 localization was detected by immunocytochemistry.
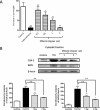
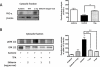
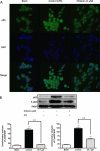
Key results: Shikonin reduced the oedema (inhibitory dose 50 = 1.0 mg per ear), the expression of cyclooxygenase-2 (70%) and of inducible nitric oxide synthase (100%) in vivo. It significantly decreased TPA-induced translocation of protein kinase Calpha, the phosphorylation and activation of ERK, the nuclear translocation of NF-kappaB and the TPA-induced NF-kappaB-DNA-binding activity in mouse skin. Moreover, in RAW 264.7 cells, shikonin significantly inhibited the binding of NF-kappaB to DNA in a dose-dependent manner and the nuclear translocation of p65.
Conclusions and implications: Shikonin exerted its topical anti-inflammatory action by interfering with the degradation of IkappaBalpha, thus inhibiting the activation of NF-kappaB.
Figures




References
-
- Afaq F, Saleem M, Aziz MH, Mukhtar H. Inhibition of 12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol-13-acetate-induced tumor promotion markers in CD-1 mouse skin by oleandrin. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2004;195(3):361–369. - PubMed
-
- Baeuerle PA. IkB-NF-κB structures: at the interface of inflammation control. Cell. 1998;95:729–731. - PubMed
-
- Baeuerle PA, Baltimore D. NF-κB: ten years after. Cell. 1996;87:13–20. - PubMed
-
- Baggiolini M. Chemokines and leukocyte traffic. Nature. 1998;392:565–568. - PubMed
-
- Bell S, Degitz K, Quirling M, Jilg N, Page S, Brand K. Involvement of NF-κB signalling in skin physiology and disease. Cell Signal. 2003;15:1–7. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

