Change in basic motor abilities, quality of movement and everyday activities following intensive, goal-directed, activity-focused physiotherapy in a group setting for children with cerebral palsy
- PMID: 20423507
- PMCID: PMC2878295
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2431-10-26
Change in basic motor abilities, quality of movement and everyday activities following intensive, goal-directed, activity-focused physiotherapy in a group setting for children with cerebral palsy
Abstract
Background: The effects of intensive training for children with cerebral palsy (CP) remain uncertain. The aim of the study was to investigate the impact on motor function, quality of movements and everyday activities of three hours of goal-directed activity-focused physiotherapy in a group setting, five days a week for a period of three weeks.
Methods: A repeated measures design was applied with three baseline and two follow up assessments; immediately and three weeks after intervention. Twenty-two children with hemiplegia (n = 7), diplegia (n = 11), quadriplegia (n = 2) and ataxia (n = 2) participated, age ranging 3-9 y. All levels of Gross Motor Function Classification System (GMFCS) and Manual Ability Classification System (MACS) were represented. Parents and professionals participated in goal setting and training. ANOVA was used to analyse change over repeated measures.
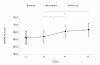
Results: A main effect of time was shown in the primary outcome measure; Gross Motor Function Measure-66 (GMFM-66), mean change being 4.5 (p < 0.01) from last baseline to last follow up assessment. An interaction between time and GMFCS-levels was found, implying that children classified to GMFCS-levels I-II improved more than children classified to levels III-V. There were no main or interaction effects of age or anti-spastic medication. Change scores in the Pediatric Evaluation of Disability Inventory (PEDI) ranged 2.0-6.7, p < 0.01 in the Self-care domain of the Functional Skills dimension, and the Self-care and Mobility domains of the Caregiver Assistance dimension. The children's individual goals were on average attained, Mean Goal Attainment Scaling (GAS) T-score being 51.3. Non-significant improved scores on the Gross Motor Performance Measure (GMPM) and the Quality of Upper Extremities Skills Test (QUEST) were demonstrated. Significant improvement in GMPM scores were found in improved items of the GMFM, not in items that maintained the same score.
Conclusions: Basic motor abilities and self-care improved in young children with CP after goal-directed activity-focused physiotherapy with involvement of their local environment, and their need for caregiver assistance in self-care and mobility decreased. The individualized training within a group context during a limited period of time was feasible and well-tolerated. The coherence between acquisition of basic motor abilities and quality of movement should be further examined.
Figures
References
-
- Rosenbaum P, Paneth N, Leviton A, Goldstein M, Bax M. A report: the definition and classification of cerebral palsy April 2006. Dev Med Child Neurol Suppl. 2007;109:8–14. - PubMed
-
- World Health Organization. International Classification of Functioning, Disability and Health. Children & Youth Version. Geneva, WHO; 2007.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous