Comparison of ATP-binding cassette transporter interactions with the tyrosine kinase inhibitors imatinib, nilotinib, and dasatinib
- PMID: 20423956
- PMCID: PMC2913625
- DOI: 10.1124/dmd.109.031302
Comparison of ATP-binding cassette transporter interactions with the tyrosine kinase inhibitors imatinib, nilotinib, and dasatinib
Abstract
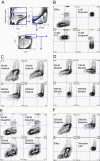
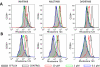
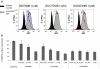
Although the development of tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs) to control the unregulated activity of BCR-ABL revolutionized the therapy of chronic myeloid leukemia, resistance to TKIs is a clinical reality. Among the postulated mechanisms of resistance is the overexpression of ATP-binding cassette (ABC) transporters, such as P-glycoprotein (ABCB1) and breast cancer resistance protein (ABCG2), which mediate reduced intracellular drug accumulation. We compared the interactions of the TKIs imatinib, nilotinib, and dasatinib with ABCB1 and ABCG2 in ex vivo and in vitro systems. The TKIs inhibited rhodamine 123 and Hoechst 33342 efflux mediated by endogenous expression of the transporters in murine and human hematopoietic stem cells with potency order nilotinib >> imatinib >> dasatinib. Studies with ABCB1-, ABCG2-, and ABCC1-transfected human embryonic kidney 293 cells verified that nilotinib was the most potent inhibitor of ABCB1 and ABCG2. Cytotoxicity assays in stably transduced K562-ABCG2 and K562-ABCB1 cells confirmed that the TKIs were also substrates for the two transporters. Like imatinib, both nilotinib and dasatinib decreased ABCG2 surface expression in K562-ABCG2 cells. Finally, we found that all TKIs were able to compete labeling of ABCB1 and ABCG2 by the photo-cross-linkable prazosin analog [(125)I]iodoarylazidoprazosin, suggesting interaction at the prazosin-binding site of both proteins. Our experiments support the hypothesis that all three TKIs are substrates of ABC transporters and that, at higher concentrations, TKIs overcome transporter function. Taken together, the results suggest that therapeutic doses of imatinib and nilotinib may diminish the potential of ABCB1 and ABCG2 to limit oral absorption or confer resistance. Clinical data are required to definitively answer the latter question.
Figures

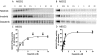

References
-
- Ambudkar SV. (1998) Drug-stimulatable ATPase activity in crude membranes of human MDR1-transfected mammalian cells. Methods Enzymol 292:504–514 - PubMed
-
- Bhatia R, Holtz M, Niu N, Gray R, Snyder DS, Sawyers CL, Arber DA, Slovak ML, Forman SJ. (2003) Persistence of malignant hematopoietic progenitors in chronic myelogenous leukemia patients in complete cytogenetic remission following imatinib mesylate treatment. Blood 101:4701–4707 - PubMed
-
- Bradeen HA, Eide CA, O'Hare T, Johnson KJ, Willis SG, Lee FY, Druker BJ, Deininger MW. (2006) Comparison of imatinib mesylate, dasatinib (BMS-354825), and nilotinib (AMN107) in an N-ethyl-N-nitrosourea (ENU)-based mutagenesis screen: high efficacy of drug combinations. Blood 108:2332–2338 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Brendel C, Scharenberg C, Dohse M, Robey RW, Bates SE, Shukla S, Ambudkar SV, Wang Y, Wennemuth G, Burchert A, et al. (2007) Imatinib mesylate and nilotinib (AMN107) exhibit high-affinity interaction with ABCG2 on primitive hematopoietic stem cells. Leukemia 21:1267–1275 - PubMed
-
- Burger H, van Tol H, Boersma AW, Brok M, Wiemer EA, Stoter G, Nooter K. (2004) Imatinib mesylate (STI571) is a substrate for the breast cancer resistance protein (BCRP)/ABCG2 drug pump. Blood 104:2940–2942 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

