Assembly, structure, and function of the 26S proteasome
- PMID: 20427185
- PMCID: PMC2902798
- DOI: 10.1016/j.tcb.2010.03.007
Assembly, structure, and function of the 26S proteasome
Abstract
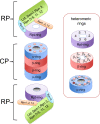
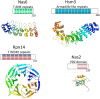
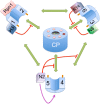
The 26S proteasome is a large multiprotein complex involved in the regulated degradation of ubiquitinated proteins in the cell. The 26S proteasome has been shown to control an increasing number of essential biochemical mechanisms of the cellular lifecycle including DNA synthesis, repair, transcription, translation, and cell signal transduction. Concurrently, it is increasingly seen that malfunction of the ubiquitin proteasome system contributes to the pathogenesis of disease. The recent identification of four molecular chaperones, in addition to five previously identified chaperones, have provided mechanistic insight into how this cellular megastructure is assembled in the cell. These data, together with new insights into the structure and function of the proteasome, provide a much better understanding of this complex protease.
Crown Copyright 2010. Published by Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Balch WE, et al. Adapting proteostasis for disease intervention. Science. 2008;319:916–919. - PubMed
-
- Murata S, et al. Molecular mechanisms of proteasome assembly. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2009;10:104–115. - PubMed
-
- Marques AJ, et al. Catalytic mechanism and assembly of the proteasome. Chem Rev. 2009;109:1509–1536. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

