Tti1 and Tel2 are critical factors in mammalian target of rapamycin complex assembly
- PMID: 20427287
- PMCID: PMC2888423
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M110.121699
Tti1 and Tel2 are critical factors in mammalian target of rapamycin complex assembly
Abstract
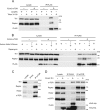
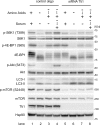
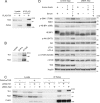
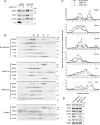
Mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) is a member of the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase-related kinase (PIKK) family and is a major regulator of translation, cell growth, and autophagy. mTOR exists in two distinct complexes, mTORC1 and mTORC2, that differ in their subunit composition. In this study, we identified KIAA0406 as a novel mTOR-interacting protein. Because it has sequence homology with Schizosaccharomyces pombe Tti1, we named it mammalian Tti1. Tti1 constitutively interacts with mTOR in both mTORC1 and mTORC2. Knockdown of Tti1 suppresses phosphorylation of both mTORC1 substrates (S6K1 and 4E-BP1) and an mTORC2 substrate (Akt) and also induces autophagy. S. pombe Tti1 binds to Tel2, a protein whose mammalian homolog was recently reported to regulate the stability of PIKKs. We confirmed that Tti1 binds to Tel2 also in mammalian cells, and Tti1 interacts with and stabilizes all six members of the PIKK family of proteins (mTOR, ATM, ATR, DNA-PKcs, SMG-1, and TRRAP). Furthermore, using immunoprecipitation and size-exclusion chromatography analyses, we found that knockdown of either Tti1 or Tel2 causes disassembly of mTORC1 and mTORC2. These results indicate that Tti1 and Tel2 are important not only for mTOR stability but also for assembly of the mTOR complexes to maintain their activities.
Figures


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

