A perisynaptic ménage à trois between Dlg, DLin-7, and Metro controls proper organization of Drosophila synaptic junctions
- PMID: 20427642
- PMCID: PMC6632599
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0778-10.2010
A perisynaptic ménage à trois between Dlg, DLin-7, and Metro controls proper organization of Drosophila synaptic junctions
Abstract
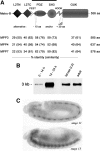
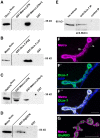
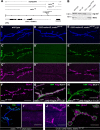
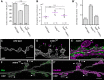
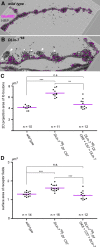
Structural plasticity of synaptic junctions is a prerequisite to achieve and modulate connectivity within nervous systems, e.g., during learning and memory formation. It demands adequate backup systems that allow remodeling while retaining sufficient stability to prevent unwanted synaptic disintegration. The strength of submembranous scaffold complexes, which are fundamental to the architecture of synaptic junctions, likely constitutes a crucial determinant of synaptic stability. Postsynaptic density protein-95 (PSD-95)/ Discs-large (Dlg)-like membrane-associated guanylate kinases (DLG-MAGUKs) are principal scaffold proteins at both vertebrate and invertebrate synapses. At Drosophila larval glutamatergic neuromuscular junctions (NMJs) DlgA and DlgS97 exert pleiotropic functions, probably reflecting a few known and a number of yet-unknown binding partners. In this study we have identified Metro, a novel p55/MPP-like Drosophila MAGUK as a major binding partner of perisynaptic DlgS97 at larval NMJs. Based on homotypic LIN-2,-7 (L27) domain interactions, Metro stabilizes junctional DlgS97 in a complex with the highly conserved adaptor protein DLin-7. In a remarkably interdependent manner, Metro and DLin-7 act downstream of DlgS97 to control NMJ expansion and proper establishment of synaptic boutons. Using quantitative 3D-imaging we further demonstrate that the complex controls the size of postsynaptic glutamate receptor fields. Our findings accentuate the importance of perisynaptic scaffold complexes for synaptic stabilization and organization.
Figures


References
-
- Aartsen WM, Kantardzhieva A, Klooster J, van Rossum AG, van de Pavert SA, Versteeg I, Cardozo BN, Tonagel F, Beck SC, Tanimoto N, Seeliger MW, Wijnholds J. Mpp4 recruits Psd95 and Veli3 towards the photoreceptor synapse. Hum Mol Genet. 2006;15:1291–1302. - PubMed
-
- Ataman B, Budnik V, Thomas U. Scaffolding proteins at the Drosophila neuromuscular junction. Int Rev Neurobiol. 2006;75:181–216. - PubMed
-
- Bachmann A, Knust E. The use of P-element transposons to generate transgenic flies. Methods Mol Biol. 2008;420:61–77. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
