The transcription factor Mef2 is required for normal circadian behavior in Drosophila
- PMID: 20427646
- PMCID: PMC2876976
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2688-09.2010
The transcription factor Mef2 is required for normal circadian behavior in Drosophila
Abstract
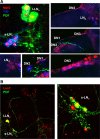
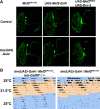
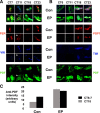
The transcription factor Mef2 has well established roles in muscle development in Drosophila and in the differentiation of many cell types in mammals, including neurons. Here, we describe a role for Mef2 in the Drosophila pacemaker neurons that regulate circadian behavioral rhythms. We found that Mef2 is normally produced in all adult clock neurons and that Mef2 overexpression in clock neurons leads to long period and complex rhythms of adult locomotor behavior. Knocking down Mef2 expression via RNAi or expressing a repressor form of Mef2 caused flies to lose circadian behavioral rhythms. These behavioral changes are correlated with altered molecular clocks in pacemaker neurons: Mef2 overexpression causes the oscillations in individual pacemaker neurons to become desynchronized, while Mef2 knockdown strongly dampens molecular rhythms. Thus, a normal level of Mef2 activity is required in clock neurons to maintain robust and accurate circadian behavioral rhythms.
Figures





References
-
- Arnold MA, Kim Y, Czubryt MP, Phan D, McAnally J, Qi X, Shelton JM, Richardson JA, Bassel-Duby R, Olson EN. MEF2C transcription factor controls chondrocyte hypertrophy and bone development. Dev Cell. 2007;12:377–389. - PubMed
-
- Berni J, Beckwith EJ, Fernández MP, Ceriani MF. The axon-guidance roundabout gene alters the pace of the Drosophila circadian clock. Eur J Neurosci. 2008;27:396–407. - PubMed
-
- Blau J, Young MW. Cycling vrille expression is required for a functional Drosophila clock. Cell. 1999;99:661–671. - PubMed
-
- Bour BA, O'Brien MA, Lockwood WL, Goldstein ES, Bodmer R, Taghert PH, Abmayr SM, Nguyen HT. Drosophila MEF2, a transcription factor that is essential for myogenesis. Genes Dev. 1995;9:730–741. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
