Dysregulation of dopamine transporters via dopamine D2 autoreceptors triggers anomalous dopamine efflux associated with attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder
- PMID: 20427663
- PMCID: PMC2881830
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.5094-09.2010
Dysregulation of dopamine transporters via dopamine D2 autoreceptors triggers anomalous dopamine efflux associated with attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder
Abstract
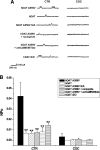
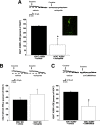
The neurotransmitter dopamine (DA) modulates brain circuits involved in attention, reward, and motor activity. Synaptic DA homeostasis is primarily controlled via two presynaptic regulatory mechanisms, DA D(2) receptor (D(2)R)-mediated inhibition of DA synthesis and release, and DA transporter (DAT)-mediated DA clearance. D(2)Rs can physically associate with DAT and regulate DAT function, linking DA release and reuptake to a common mechanism. We have established that the attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder-associated human DAT coding variant Ala559Val (hDAT A559V) results in anomalous DA efflux (ADE) similar to that caused by amphetamine-like psychostimulants. Here, we show that tonic activation of D(2)R provides support for hDAT A559V-mediated ADE. We determine in hDAT A559V a pertussis toxin-sensitive, CaMKII-dependent phosphorylation mechanism that supports D(2)R-driven DA efflux. These studies identify a signaling network downstream of D(2)R activation, normally constraining DA action at synapses, that may be altered by DAT mutation to impact risk for DA-related disorders.
Figures




References
-
- Bannon MJ. 2004. Dopamine. Nature Encyclopedia of Life Sciences, Nature Publishing Group. Retrieved May 15, 2008 from www.els.net.
-
- Bannon MJ, Sacchetti P, Granneman JG. The dopamine transporter: potential involvement in neuropsychiatric disorders. In: Watson SJ, editor. Psychopharmacology: the fourth generation of progress. Nashville, TN: The American College of Neuropsychopharmacology; 2000.
-
- Bolan EA, Kivell B, Jaligam V, Oz M, Jayanthi LD, Han Y, Sen N, Urizar E, Gomes I, Devi LA, Ramamoorthy S, Javitch JA, Zapata A, Shippenberg TS. D2 receptors regulate dopamine transporter function via an extracellular signal-regulated kinases 1 and 2-dependent and phosphoinositide 3 kinase-independent mechanism. Mol Pharmacol. 2007;71:1222–1232. - PubMed
-
- Carlsson A. Perspectives on the discovery of central monoaminergic neurotransmission. Annu Rev Neurosci. 1987;10:19–40. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- DA13975/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH054137/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DA013975/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- MH081423/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- F31 MH081423/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- DA22413/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH058921/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- K99 DA025716/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- MH54137/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- K05 DA022413/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- DA020306/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH063232/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- P01 DA012408/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- MH58921/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- F32 DA020306/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- DA12408/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- MH63232/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R56 DA013975/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
