The P2Y2 receptor mediates the epithelial injury response and cell migration
- PMID: 20427708
- PMCID: PMC2928627
- DOI: 10.1152/ajpcell.00100.2009
The P2Y2 receptor mediates the epithelial injury response and cell migration
Abstract
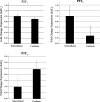
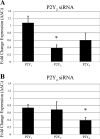
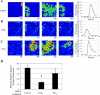
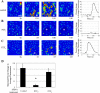
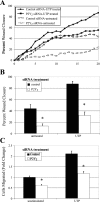
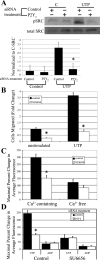
Injury to epithelial cells results in the release of ATP and stimulation of purinergic receptors and is thought to alter cell migration and wound repair. Medium from the injured cells triggers Ca(2+) mobilization and phosphorylation of ERK, both of which are inhibited if the medium is pretreated with apyrase. To understand the wound repair mechanism that occurs with injury, our goal was to determine which purinergic receptor(s) was the critical player in the wound response. We hypothesize that the P2Y(2) receptor is the key player in the response of corneal epithelial cells to cell damage and subsequent repair events. Cells transfected with short interfering RNA to either P2Y(2) or P2Y(4) were stimulated either by injury or addition of UTP and imaged using fluo 3-AM to monitor changes in fluorescence. When cells with downregulated P2Y(2) receptors were injured or stimulated with UTP, the intensity of the Ca(2+) release was reduced significantly. However, when cells with downregulated P2Y(4) receptors were stimulated, only the UTP-induced Ca(2+) response was reduced significantly. In addition, downregulation of the P2Y(2) receptor inhibited wound closure compared with unstimulated cells or cells transfected with nontargeting sequence. This downregulation resulted also in an attenuation in phosphorylation of Src and ERK. Together, these data indicate that the P2Y(2) receptor plays a major biological role in the corneal injury response and repair mechanisms.
Figures


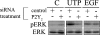
References
-
- Abbracchio MP, Burnstock G. Purinergic signalling: pathophysiological roles. Jpn J Pharmacol 78: 113–145, 1998 - PubMed
-
- Abbracchio MP, Burnstock G, Boeynaems JM, Barnard EA, Boyer JL, Kennedy C, Knight GE, Fumagalli M, Gachet C, Jacobson KA, Weisman GA. International Union of Pharmacology LVIII: Update on the P2Y G protein-coupled nucleotide receptors: from molecular mechanisms and pathophysiology to therapy. Pharmacol Rev 58: 281–341, 2006. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Arthur DB, Akassoglou K, Insel PA. P2Y2 and TrkA receptors interact with Src family kinase for neuronal differentiation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 347: 678–682, 2006 - PubMed
-
- Berridge MJ. Inositol trisphosphate and diacyglycerol: two interacting second messengers. Annu Rev Biochem 56: 159–193, 1987 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

