Mu-conotoxins as leads in the development of new analgesics
- PMID: 20428082
- PMCID: PMC6257286
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules15042825
Mu-conotoxins as leads in the development of new analgesics
Abstract
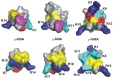
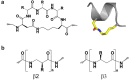
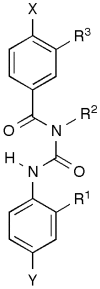
Voltage-gated sodium channels (VGSCs) contain a specific binding site for a family of cone shell toxins known as mu-conotoxins. As some VGSCs are involved in pain perception and mu-conotoxins are able to block these channels, mu-conotoxins show considerable potential as analgesics. Recent studies have advanced our understanding of the three-dimensional structures and structure-function relationships of the mu-conotoxins, including their interaction with VGSCs. Truncated peptide analogues of the native toxins have been created in which secondary structure elements are stabilized by non-native linkers such as lactam bridges. Ultimately, it would be desirable to capture the favourable analgesic properties of the native toxins, in particular their potency and channel sub-type selectivity, in non-peptide mimetics. Such mimetics would constitute lead compounds in the development of new therapeutics for the treatment of pain.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Structure of the analgesic mu-conotoxin KIIIA and effects on the structure and function of disulfide deletion.Biochemistry. 2009 Feb 17;48(6):1210-9. doi: 10.1021/bi801998a. Biochemistry. 2009. PMID: 19170536 Free PMC article.
-
Conotoxin modulation of voltage-gated sodium channels.Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2008;40(11):2363-8. doi: 10.1016/j.biocel.2007.08.017. Epub 2007 Sep 14. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2008. PMID: 17951097 Review.
-
Structure and function of μ-conotoxins, peptide-based sodium channel blockers with analgesic activity.Future Med Chem. 2014 Oct;6(15):1677-98. doi: 10.4155/fmc.14.107. Future Med Chem. 2014. PMID: 25406007 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Lactam-stabilized helical analogues of the analgesic μ-conotoxin KIIIA.J Med Chem. 2011 Nov 10;54(21):7558-66. doi: 10.1021/jm200839a. Epub 2011 Oct 12. J Med Chem. 2011. PMID: 21962108 Free PMC article.
-
Conotoxins targeting neuronal voltage-gated sodium channel subtypes: potential analgesics?Toxins (Basel). 2012 Nov 8;4(11):1236-60. doi: 10.3390/toxins4111236. Toxins (Basel). 2012. PMID: 23202314 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Molecular dynamics study of binding of µ-conotoxin GIIIA to the voltage-gated sodium channel Na(v)1.4.PLoS One. 2014 Aug 18;9(8):e105300. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0105300. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 25133704 Free PMC article.
-
A novel µ-conopeptide, CnIIIC, exerts potent and preferential inhibition of NaV1.2/1.4 channels and blocks neuronal nicotinic acetylcholine receptors.Br J Pharmacol. 2012 Jul;166(5):1654-68. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.2012.01837.x. Br J Pharmacol. 2012. PMID: 22229737 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanism of μ-conotoxin PIIIA binding to the voltage-gated Na+ channel NaV1.4.PLoS One. 2014 Mar 27;9(3):e93267. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0093267. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24676211 Free PMC article.
-
Computational studies of marine toxins targeting ion channels.Mar Drugs. 2013 Mar 13;11(3):848-69. doi: 10.3390/md11030848. Mar Drugs. 2013. PMID: 23528952 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Strategies for the development of conotoxins as new therapeutic leads.Mar Drugs. 2013 Jun 28;11(7):2293-313. doi: 10.3390/md11072293. Mar Drugs. 2013. PMID: 23812174 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Norton R.S., Olivera B.M. Conotoxins down under. Toxicon. 2006;48:780–798. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

