Polymorphisms in DNA damage response genes and head and neck cancer risk
- PMID: 20429839
- PMCID: PMC2907474
- DOI: 10.3109/13547501003797664
Polymorphisms in DNA damage response genes and head and neck cancer risk
Abstract
Background: Polymorphisms in DNA repair genes have been reported contributing factors in head and neck cancer risk but studies have shown conflicting results.
Objective: To clarify the impact of DNA repair gene polymorphisms in head and neck cancer risk.
Method: A meta-analysis including 30 case-control studies was performed.
Results: Marginally statistically significant association was found for XRCC1 codon 399 (for Caucasians only), XPD Asp312Asn and XRCC1 codon 194 variants and head and neck cancer.
Conclusion: Assessments of the effects of smoking, alcohol, human papillomavirus and race/ethnicity on the association between DNA repair gene polymorphisms and head and neck cancer are needed.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

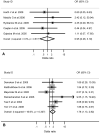
References
-
- Abbasi R, Ramroth H, Becher H, Dietz A, Schmezer P, Popanda O. Laryngeal cancer risk associated with smoking and alcohol consumption is modified by genetic polymorphisms in ERCC5, ERCC6 and RAD23B but not by polymorphisms in five other nucleotide excision repair genes. Int J Cancer. 2009;125:1431–9. - PubMed
-
- Altieri F, Grillo C, Maceroni M, Chichiarelli S. DNA damage and repair: from molecular mechanisms to health implications. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2008;10:891–937. - PubMed
-
- An J, Liu Z, Hu Z, Li G, Wang LE, Sturgis EM, El-Naggar AK, Spitz MR, Wei Q. Potentially functional single nucleotide polymorphisms in the core nucleotide excision repair genes and risk of squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 2007;16:1633–8. - PubMed
-
- Arbes SJ, Jr, Olshan AF, Caplan DJ, Schoenbach VJ, Slade GD, Symons MJ. Factors contributing to the poorer survival of black Americans diagnosed with oral cancer (United States) Cancer Causes Control. 1999;10:513–23. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
