Progress in the use of RNA interference as a therapy for chronic hepatitis B virus infection
- PMID: 20429960
- PMCID: PMC2873806
- DOI: 10.1186/gm149
Progress in the use of RNA interference as a therapy for chronic hepatitis B virus infection
Abstract
Chronic infection with hepatitis B virus (HBV) occurs in approximately 6% of the world's population and carriers of the virus are at risk for hepatocellular carcinoma and cirrhosis. Current treatment regimens, which include interferon-alpha and nucleoside/nucleotide analogs, are only partially effective and new treatment methods remain an important objective. Harnessing the RNA interference (RNAi) pathway to achieve post-transcriptional silencing of rogue genetic elements is an exciting avenue for development of novel therapeutic strategies. The specific and potent suppression of HBV gene expression and replication is an attractive option as a novel and effective approach for the treatment of chronic HBV infection. However, despite significant and rapid progress, existing RNAi technologies require further refinement before clinical applications can be realized. Here, we review current efforts aimed at improving the efficiency of anti-HBV RNAi-based delivery systems, at limiting the toxicities associated with RNAi modalities and at preventing reactivation of viral replication. We discuss the progress towards clinical implementation of anti-HBV RNAi therapies.
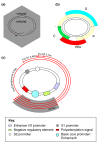
Figures
References
-
- Allen MI, Deslauriers M, Andrews CW, Tipples GA, Walters KA, Tyrrell DL, Brown N, Condreay LD. Identification and characterization of mutations in hepatitis B virus resistant to lamivudine. Lamivudine Clinical Investigation Group. Hepatology. 1998;27:1670–1677. doi: 10.1002/hep.510270628. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Terrault NA. Benefits and risks of combination therapy for hepatitis B. Hepatology. 2009;49(Suppl 5):S122–S128. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

