Site-specific effects on respiratory rhythm and pattern of ibotenic acid injections in the pontine respiratory group of goats
- PMID: 20431022
- PMCID: PMC2904194
- DOI: 10.1152/japplphysiol.00934.2009
Site-specific effects on respiratory rhythm and pattern of ibotenic acid injections in the pontine respiratory group of goats
Abstract
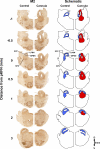
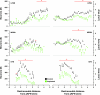
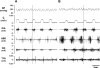
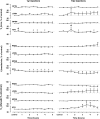
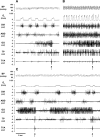
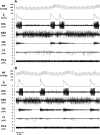
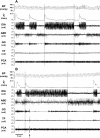
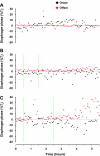
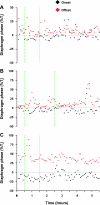
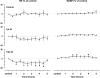
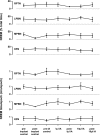
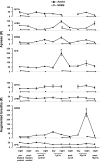
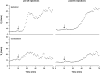
To probe further the contributions of the rostral pons to eupneic respiratory rhythm and pattern, we tested the hypothesis that ibotenic acid (IA) injections in the pontine respiratory group (PRG) would disrupt eupneic respiratory rhythm and pattern in a site- and state-specific manner. In 15 goats, cannulas were bilaterally implanted into the rostral pontine tegmental nuclei (RPTN; n = 3), the lateral (LPBN; n = 4) or medial parabrachial nuclei (MPBN; n = 4), or the Kölliker-Fuse nucleus (KFN; n = 4). After recovery from surgery, 1- and 10-microl injections (1 wk apart) of IA were made bilaterally through the implanted cannulas during the day. Over the first 5 h after the injections, there were site-specific ventilatory effects, with increased (P < 0.05) breathing frequency in RPTN-injected goats, increased (P < 0.05) pulmonary ventilation (Vi) in LPBN-injected goats, no effect (P < 0.05) in MPBN-injected goats, and a biphasic Vi response (P < 0.05) in KFN-injected goats. This biphasic response consisted of a hyperpnea for 30 min, followed by a prolonged hypopnea and hypoventilation with marked apneas, apneusis-like breathing patterns, and/or shifts in the temporal relationships between inspiratory flow and diaphragm activity. In the awake state, 10-15 h after the 1-microl injections, the number of apneas was greater (P < 0.05) than during other studies at night. However, there were no incidences of terminal apneas. Breathing rhythm and pattern were normal 22 h after the injections. Subsequent histological analysis revealed that for goats with cannulas implanted into the KFN, there were nearly 50% fewer neurons (P < 0.05) in all three PRG subnuclei than in control goats. We conclude that in awake goats, 1) IA injections into the PRG have site-specific effects on breathing, and 2) the KFN contributes to eupneic respiratory pattern generation.
Figures




References
-
- Bellingham M, Funk G. Cholinergic modulation of respiratory brain-stem neurons and its function in sleep-wake state determination. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol 27: 132– 137, 2000 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

