Targeted Vezf1-null mutation impairs vascular structure formation during embryonic stem cell differentiation
- PMID: 20431070
- PMCID: PMC2903440
- DOI: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.109.200428
Targeted Vezf1-null mutation impairs vascular structure formation during embryonic stem cell differentiation
Abstract
Objective: Vezf1 encodes an early zinc finger transcription factor that is essential for normal vascular development and functions in a dose-dependent manner. Here, we investigated the role of Vezf1 during processes of endothelial cell differentiation and maturation by studying mutant Vezf1 embryonic stem (ES) cells using the in vitro embryoid body differentiation model and the in vivo teratocarcinoma model.
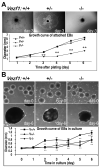
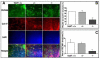
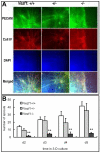
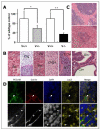
Methods and results: Vezf1-/- ES cell-derived embryoid bodies failed to form a well-organized vascular network and showed dramatic vascular sprouting defects. Our results indicate that the retinol pathway is an important mediator of Vezf1 function and that loss of Vezf1 results in reduced retinol/vitamin A signaling and aberrant extracellular matrix (ECM) formation. Unexpectedly, we also uncovered defects during in vitro differentiation of Vezf1-/- ES cells along hematopoietic cell lineages. Vezf1-/- ES cell-derived teratocarcinomas were able to spontaneously differentiate into cell types of all 3 germ layers. However, histological and immunohistochemical examination of these tumors showed decreased cell proliferation, delayed differentiation, and large foci of cells with extensive deposition of ECM. Embryoid bodies and teratocarcinomas derived from heterozygous ES cells displayed an intermediate phenotype.
Conclusions: Together, these results suggest that Vezf1 is involved in early differentiation processes of the vasculature by regulating cell differentiation, proliferation, and ECM distribution and deposition.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Reduced blood vessel formation and tumor growth in alpha5-integrin-negative teratocarcinomas and embryoid bodies.Cancer Res. 2001 Jul 1;61(13):5255-61. Cancer Res. 2001. PMID: 11431367
-
The transcription factor Vezf1 represses the expression of the antiangiogenic factor Cited2 in endothelial cells.J Biol Chem. 2018 Jul 13;293(28):11109-11118. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA118.002911. Epub 2018 May 24. J Biol Chem. 2018. PMID: 29794136 Free PMC article.
-
Vascular endothelial zinc finger 1 is involved in the regulation of angiogenesis: possible contribution of stathmin/OP18 as a downstream target gene.Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2004 May;24(5):878-84. doi: 10.1161/01.ATV.0000126373.52450.32. Epub 2004 Mar 18. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2004. PMID: 15031128
-
Role of HOXA9 and VEZF1 in endothelial biology.J Vasc Res. 2013;50(4):265-78. doi: 10.1159/000353287. Epub 2013 Jul 5. J Vasc Res. 2013. PMID: 23921720 Review.
-
Current knowledge of Krüppel-like factor 5 and vascular remodeling: providing insights for therapeutic strategies.J Mol Cell Biol. 2021 May 7;13(2):79-90. doi: 10.1093/jmcb/mjaa080. J Mol Cell Biol. 2021. PMID: 33493334 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Vezf1 regulates cardiac structure and contractile function.EBioMedicine. 2020 Jan;51:102608. doi: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2019.102608. Epub 2020 Jan 3. EBioMedicine. 2020. PMID: 31911272 Free PMC article.
-
ETV2-TET1/TET2 Complexes Induce Endothelial Cell-Specific Robo4 Expression via Promoter Demethylation.Sci Rep. 2018 Apr 4;8(1):5653. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-23937-8. Sci Rep. 2018. PMID: 29618782 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNAs: Important Regulators of Induced Pluripotent Stem Cell Generation and Differentiation.Stem Cell Rev Rep. 2018 Feb;14(1):71-81. doi: 10.1007/s12015-017-9785-6. Stem Cell Rev Rep. 2018. PMID: 29143183 Review.
-
Application of Induced Pluripotent Stem Cell-Derived Models for Investigating microRNA Regulation in Developmental Processes.Front Genet. 2022 May 26;13:899831. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2022.899831. eCollection 2022. Front Genet. 2022. PMID: 35719367 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Transcriptional mapping of the macaque retina and RPE-choroid reveals conserved inter-tissue transcription drivers and signaling pathways.Front Genet. 2022 Nov 25;13:949449. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2022.949449. eCollection 2022. Front Genet. 2022. PMID: 36506320 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Carmeliet P. Mechanisms of angiogenesis and arteriogenesis. Nat Med. 2000;6:389–395. - PubMed
-
- Risau W. Mechanisms of angiogenesis. Nature. 1997;386:671–674. - PubMed
-
- Carmeliet P, Jain RK. Angiogenesis in cancer and other diseases. Nature. 2000;407:249–257. - PubMed
-
- Carmeliet P. Angiogenesis in life, disease and medicine. Nature. 2005;438:932–936. - PubMed
-
- Jain RK. Molecular regulation of vessel maturation. Nat Med. 2003;9:685–693. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

