Intracellular trafficking of ceramide by ceramide transfer protein
- PMID: 20431265
- PMCID: PMC3417804
- DOI: 10.2183/pjab.86.426
Intracellular trafficking of ceramide by ceramide transfer protein
Abstract
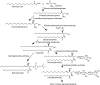
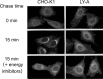
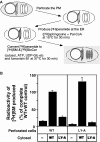
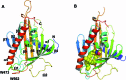
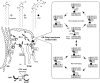
The transport and sorting of lipids are fundamental to membrane biogenesis. In the synthesis of sphingolipids in mammalian cells, ceramide is newly produced at the endoplasmic reticulum (ER), and transported from the ER to the trans Golgi regions, where it is converted to sphingomyelin. Ceramide transfer protein (CERT) mediates the ER-to-Golgi trafficking of ceramide. It has been suggested that CERT extracts ceramide from the ER and carries it to the Golgi apparatus in a non-vesicular manner and that efficient CERT-mediated trafficking of ceramide occurs at membrane contact sites between the ER and the Golgi apparatus.
Figures

References
-
- Lee M. C., Miller E. A., Goldberg J., Orci L., Schekman R. (2004) Bi-directional protein transport between the ER and Golgi. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 20, 87–123 - PubMed
-
- Watson P, Stephens D. J. (2005) ER-to-Golgi transport: form and formation of vesicular and tubular carriers. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1744, 304–315 - PubMed
-
- Pagano R. E., Puri V., Dominguez M., Marks D. L. (2000) Membrane traffic in sphingolipid storage diseases. Traffic 1, 807–815 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

