Liver transplantation
- PMID: 20431740
- PMCID: PMC2852711
- DOI: 10.5009/gnl.2009.3.3.145
Liver transplantation
Abstract
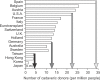
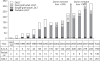
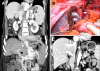
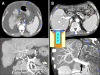
Liver transplantation has become a lifesaving procedure for patients who have chronic end-stage liver disease and acute liver failure. The satisfactory outcome of liver transplantation has led to insufficient supplies of deceased donor organs, particularly in East Asia. Hence, East Asian surgeons are concentrating on developing and performing living-donor liver transplantation (LDLT). This review article describes an update on the present status of liver transplantation, mainly in adults, and highlights some recent developments on indications for transplantation, patient selection, donor and recipient operation between LDLT and deceased-donor liver transplantation (DDLT), immunosuppression, and long-term management of liver transplant recipients. Currently, the same indication criteria that exist for DDLT are applied to LDLT, with technical refinements for LDLT. In highly experienced centers, LDLT for high-scoring (>30 points) Model of End-Stage Liver Disease (MELD) patients and acute-on-chronic liver-failure patients yields comparably good outcomes to DDLT, because timely liver transplantation with good-quality grafting is possible. With increasing numbers of liver transplantations and long-term survivors, specialized attention should be paid to complications that develop in the long term, such as chronic renal failure, hypertension, diabetes mellitus, dyslipidemia, obesity, bone or neurological complications, and development of de novo tumors, which are highly related to the immunosuppressive treatment.
Keywords: Deceased donor liver transplantation; Liver transplantation; Living donor liver transplantation.
Figures









References
-
- Ahmed A, Keeffe EB. Current indications and contraindications for liver transplantation. Clin Liver Dis. 2007;11:227–247. - PubMed
-
- Murray KR, Carithers RL., Jr AASLD practice guidelines: evaluation of the patient for liver transplantation. Hepatology. 2005;41:1407–1432. - PubMed
-
- Consensus Conference: Indications for Liver Transplantation, January 19 and 20, 2005, Lyon-Palais Des Congrès: text of recommendations (long version) Liver Transpl. 2006;12:998–1011. - PubMed
-
- National Institutes of Health Consensus Development Conference Statement: liver transplantation--June 20-23, 1983. Hepatology. 1984;4:107S–110S. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

