Dynamic susceptibility contrast MRI with localized arterial input functions
- PMID: 20432301
- PMCID: PMC3014609
- DOI: 10.1002/mrm.22338
Dynamic susceptibility contrast MRI with localized arterial input functions
Abstract
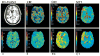
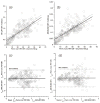
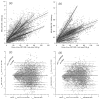
Compared to gold-standard measurements of cerebral perfusion with positron emission tomography using H(2)[(15)O] tracers, measurements with dynamic susceptibility contrast MR are more accessible, less expensive, and less invasive. However, existing methods for analyzing and interpreting data from dynamic susceptibility contrast MR have characteristic disadvantages that include sensitivity to incorrectly modeled delay and dispersion in a single, global arterial input function. We describe a model of tissue microcirculation derived from tracer kinetics that estimates for each voxel a unique, localized arterial input function. Parameters of the model were estimated using Bayesian probability theory and Markov-chain Monte Carlo, circumventing difficulties arising from numerical deconvolution. Applying the new method to imaging studies from a cohort of 14 patients with chronic, atherosclerotic, occlusive disease showed strong correlations between perfusion measured by dynamic susceptibility contrast MR with localized arterial input function and perfusion measured by quantitative positron emission tomography with H(2)[(15)O]. Regression to positron emission tomography measurements enabled conversion of dynamic susceptibility contrast MR to a physiologic scale. Regression analysis for localized arterial input function gave estimates of a scaling factor for quantitation that described perfusion accurately in patients with substantial variability in hemodynamic impairment.
(c) 2010 Wiley-Liss, Inc.
Figures


References
-
- Grubb RL, Jr, Derdeyn CP, Fritsch SM, Carpenter DA, Yundt KD, Videen TO, Spitznagel EL, Powers WJ. Importance of hemodynamic factors in the prognosis of symptomatic carotid occlusion. JAMA. 1998;280(12):1055–1060. - PubMed
-
- Gonzalez RG. Acute ischemic stroke : imaging and intervention. Berlin: Springer; 2005. p. xii.p. 268.
-
- Zazulia AR, Markham J, Powers WJ. Cerebral blood flow and metabolism in human cerebrovascular disease. In: Mohr JP, editor. Stroke: Pathophysiology, Diagnosis, and Management. Churchill and Livingstone; 2004.
-
- Powers WJ, Raichle ME, Grubb RL., Jr Positron emission tomography to assess cerebral perfusion. Lancet. 1985;1(8420):102–103. - PubMed
-
- Powers WJ, Zazulia AR. The use of Positron Emission Tomography in cerebrovascular disease. Neuroimag Clin N Am. 2003;13:741–758. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

