Toll-like receptor 2 signaling in CD4(+) T lymphocytes promotes T helper 17 responses and regulates the pathogenesis of autoimmune disease
- PMID: 20434372
- PMCID: PMC2878917
- DOI: 10.1016/j.immuni.2010.04.010
Toll-like receptor 2 signaling in CD4(+) T lymphocytes promotes T helper 17 responses and regulates the pathogenesis of autoimmune disease
Abstract
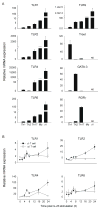
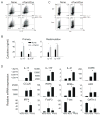
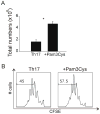
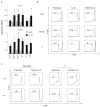
Toll-like receptors (TLRs) have previously been shown to play critical roles in the activation of innate immunity. Here, we describe that T cell expression of TLR2 regulates T helper 17 (Th17) cell responses. Stimulation with TLR2 agonists promoted Th17 differentiation in vitro and led to more robust proliferation and Th17 cytokine production. Using the experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis (EAE) model, we found that TLR2 regulated Th17 cell-mediated autoimmunity in vivo and that loss of TLR2 in CD4(+) T cells dramatically ameliorated EAE. This study thus reveals a critical role of a TLR in the direct regulation of adaptive immune response and pathogenesis of autoimmune diseases.
Copyright 2010 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Brustle A, Heink S, Huber M, Rosenplanter C, Stadelmann C, Yu P, Arpaia E, Mak TW, Kamradt T, Lohoff M. The development of inflammatory T(H)-17 cells requires interferon-regulatory factor 4. Nat Immunol. 2007;8:958–966. - PubMed
-
- Cottalorda A, Verschelde C, Marcais A, Tomkowiak M, Musette P, Uematsu S, Akira S, Marvel J, Bonnefoy-Berard N. TLR2 engagement on CD8 T cells lowers the threshold for optimal antigen-induced T cell activation. Eur J Immunol. 2006;36:1684–1693. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

