Remodeling the cortex in memory: Increased use of a learning strategy increases the representational area of relevant acoustic cues
- PMID: 20434577
- PMCID: PMC2922489
- DOI: 10.1016/j.nlm.2010.04.009
Remodeling the cortex in memory: Increased use of a learning strategy increases the representational area of relevant acoustic cues
Abstract
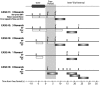
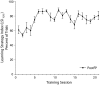
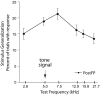
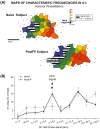
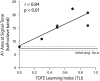
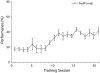
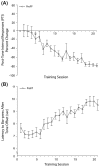
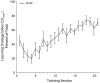
Associative learning induces plasticity in the representation of sensory information in sensory cortices. Such high-order associative representational plasticity (HARP) in the primary auditory cortex (A1) is a likely substrate of auditory memory: it is specific, rapidly acquired, long-lasting and consolidates. Because HARP is likely to support the detailed content of memory, it is important to identify the necessary behavioral factors that dictate its induction. Learning strategy is a critical factor for the induction of plasticity (Bieszczad & Weinberger, 2010b). Specifically, use of a strategy that relies on tone onsets induces HARP in A1 in the form of signal-specific decreased threshold and bandwidth. The present study tested the hypothesis that the form and degree of HARP in A1 reflects the amount of use of an "onset strategy". Adult male rats (n=7) were trained in a protocol that increased the use of this strategy from approximately 20% in prior studies to approximately 80%. They developed signal-specific gains in representational area, transcending plasticity in the form of local changes in threshold and bandwidth. Furthermore, the degree of area gain was proportional to the amount of use of the onset strategy. A second complementary experiment demonstrated that use of a learning strategy that specifically did not rely on tone onsets did not produce gains in representational area; but rather produced area loss. Together, the findings indicate that the amount of strategy use is a dominant factor for the induction of learning-induced cortical plasticity along a continuum of both form and degree.
Copyright 2010 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Learning strategy trumps motivational level in determining learning-induced auditory cortical plasticity.Neurobiol Learn Mem. 2010 Feb;93(2):229-39. doi: 10.1016/j.nlm.2009.10.003. Epub 2009 Oct 21. Neurobiol Learn Mem. 2010. PMID: 19853056 Free PMC article.
-
Learning strategy determines auditory cortical plasticity.Neurobiol Learn Mem. 2008 Feb;89(2):153-66. doi: 10.1016/j.nlm.2007.07.004. Epub 2007 Aug 17. Neurobiol Learn Mem. 2008. PMID: 17707663 Free PMC article.
-
Representational gain in cortical area underlies increase of memory strength.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010 Feb 23;107(8):3793-8. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1000159107. Epub 2010 Feb 4. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010. PMID: 20133679 Free PMC article.
-
New perspectives on the auditory cortex: learning and memory.Handb Clin Neurol. 2015;129:117-47. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-444-62630-1.00007-X. Handb Clin Neurol. 2015. PMID: 25726266 Review.
-
Auditory associative memory and representational plasticity in the primary auditory cortex.Hear Res. 2007 Jul;229(1-2):54-68. doi: 10.1016/j.heares.2007.01.004. Epub 2007 Jan 17. Hear Res. 2007. PMID: 17344002 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Psychological and neural mechanisms of experimental extinction: a selective review.Neurobiol Learn Mem. 2014 Feb;108:38-51. doi: 10.1016/j.nlm.2013.09.016. Epub 2013 Oct 6. Neurobiol Learn Mem. 2014. PMID: 24104049 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Spectral plasticity in monkey primary auditory cortex limits performance generalization in a temporal discrimination task.J Neurophysiol. 2020 Dec 1;124(6):1798-1814. doi: 10.1152/jn.00278.2020. Epub 2020 Sep 30. J Neurophysiol. 2020. PMID: 32997564 Free PMC article.
-
Neural encoding of sensory and behavioral complexity in the auditory cortex.Curr Opin Neurobiol. 2018 Oct;52:65-71. doi: 10.1016/j.conb.2018.04.002. Epub 2018 Apr 27. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 2018. PMID: 29709885 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Acute and Long-Term Circuit-Level Effects in the Auditory Cortex After Sound Trauma.Front Neurosci. 2021 Jan 5;14:598406. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2020.598406. eCollection 2020. Front Neurosci. 2021. PMID: 33469416 Free PMC article.
-
Extinction reveals that primary sensory cortex predicts reinforcement outcome.Eur J Neurosci. 2012 Feb;35(4):598-613. doi: 10.1111/j.1460-9568.2011.07974.x. Epub 2012 Feb 3. Eur J Neurosci. 2012. PMID: 22304434 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bakin JS, South DA, Weinberger NM. Induction of receptive field plasticity in the auditory cortex of the guinea pig during instrumental avoidance conditioning. Behavioral Neuroscience. 1996;110(5):905–913. - PubMed
-
- Bakin JS, Weinberger NM. Classical conditioning induces CS-specific receptive field plasticity in the auditory cortex of the guinea pig. Brain Research. 1990;536(1–2):271–286. - PubMed
-
- Bao S, Chang EF, Woods J, Merzenich MM. Temporal plasticity in the primary auditory cortex induced by operant perceptual learning. Nature Neuroscience. 2004;7(9):974–981. - PubMed
-
- Beitel RE, Schreiner CE, Cheung SW, Wang X, Merzenich MM. Reward-dependent plasticity in the primary auditory cortex of adult monkeys trained to discriminate temporally modulated signals. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 2003;100(19):11070–11075. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

