c-Myc regulates transcriptional pause release
- PMID: 20434984
- PMCID: PMC2864022
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2010.03.030
c-Myc regulates transcriptional pause release
Abstract
Recruitment of the RNA polymerase II (Pol II) transcription initiation apparatus to promoters by specific DNA-binding transcription factors is well recognized as a key regulatory step in gene expression. We report here that promoter-proximal pausing is a general feature of transcription by Pol II in mammalian cells and thus an additional step where regulation of gene expression occurs. This suggests that some transcription factors recruit the transcription apparatus to promoters, whereas others effect promoter-proximal pause release. Indeed, we find that the transcription factor c-Myc, a key regulator of cellular proliferation, plays a major role in Pol II pause release rather than Pol II recruitment at its target genes. We discuss the implications of these results for the role of c-Myc amplification in human cancer.
2010 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
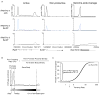
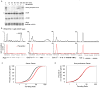
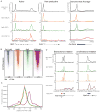
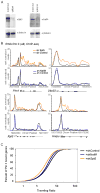
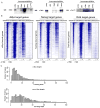
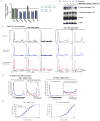
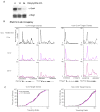
Comment in
-
Regulation of RNA polymerase II elongation by c-Myc.Cell. 2010 Apr 30;141(3):399-400. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2010.04.016. Cell. 2010. PMID: 20434979
-
Adding more to the Myc story.Nat Rev Cancer. 2010 Jul;10(7):455. doi: 10.1038/nrc2879. Nat Rev Cancer. 2010. PMID: 20589974 No abstract available.
References
-
- Ahn SH, Kim M, Buratowski S. Phosphorylation of serine 2 within the RNA polymerase II C-terminal domain couples transcription and 3′ end processing. Mol Cell. 2004;13:67–76. - PubMed
-
- Barboric M, Nissen RM, Kanazawa S, Jabrane-Ferrat N, Peterlin BM. NF-kappaB binds P-TEFb to stimulate transcriptional elongation by RNA polymerase II. Mol Cell. 2001;8:327–337. - PubMed
-
- Bentley DL, Groudine M. A block to elongation is largely responsible for decreased transcription of c-myc in differentiated HL60 cells. Nature. 1986;321:702–706. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
- R01 CA146445/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P01 CA042063/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA014051/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30-CA14051/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM034277/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- F32 HD051190/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- P01-CA42063/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HG002668/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- R01-GM34277/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01-HG002668/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- R01-CA133404/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- 5-F32-HD051190/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- R37 GM034277/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA133404/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

