Lipoprotein-associated phospholipase A(2) and risk of coronary disease, stroke, and mortality: collaborative analysis of 32 prospective studies
- PMID: 20435228
- PMCID: PMC2864403
- DOI: 10.1016/S0140-6736(10)60319-4
Lipoprotein-associated phospholipase A(2) and risk of coronary disease, stroke, and mortality: collaborative analysis of 32 prospective studies
Abstract
Background: Lipoprotein-associated phospholipase A(2) (Lp-PLA(2)), an inflammatory enzyme expressed in atherosclerotic plaques, is a therapeutic target being assessed in trials of vascular disease prevention. We investigated associations of circulating Lp-PLA(2) mass and activity with risk of coronary heart disease, stroke, and mortality under different circumstances.
Methods: With use of individual records from 79 036 participants in 32 prospective studies (yielding 17 722 incident fatal or non-fatal outcomes during 474 976 person-years at risk), we did a meta-analysis of within-study regressions to calculate risk ratios (RRs) per 1 SD higher value of Lp-PLA(2) or other risk factor. The primary outcome was coronary heart disease.
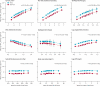
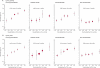
Findings: Lp-PLA(2) activity and mass were associated with each other (r=0.51, 95% CI 0.47-0.56) and proatherogenic lipids. We noted roughly log-linear associations of Lp-PLA(2) activity and mass with risk of coronary heart disease and vascular death. RRs, adjusted for conventional risk factors, were: 1.10 (95% CI 1.05-1.16) with Lp-PLA(2) activity and 1.11 (1.07-1.16) with Lp-PLA(2) mass for coronary heart disease; 1.08 (0.97-1.20) and 1.14 (1.02-1.27) for ischaemic stroke; 1.16 (1.09-1.24) and 1.13 (1.05-1.22) for vascular mortality; and 1.10 (1.04-1.17) and 1.10 (1.03-1.18) for non-vascular mortality, respectively. RRs with Lp-PLA(2) did not differ significantly in people with and without initial stable vascular disease, apart from for vascular death with Lp-PLA(2) mass. Adjusted RRs for coronary heart disease were 1.10 (1.02-1.18) with non-HDL cholesterol and 1.10 (1.00-1.21) with systolic blood pressure.
Interpretation: Lp-PLA(2) activity and mass each show continuous associations with risk of coronary heart disease, similar in magnitude to that with non-HDL cholesterol or systolic blood pressure in this population. Associations of Lp-PLA(2) mass and activity are not exclusive to vascular outcomes, and the vascular associations depend at least partly on lipids.
Funding: UK Medical Research Council, GlaxoSmithKline, and British Heart Foundation.
Copyright 2010 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures


Comment in
-
Lp-PLA(2) and risk of atherosclerotic vascular disease.Lancet. 2010 May 1;375(9725):1498-500. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(10)60488-6. Lancet. 2010. PMID: 20435213 No abstract available.
References
-
- Kolodgie FD, Burke AP, Skorija KS. Lipoprotein-associated phospholipase A2 protein expression in the natural progression of human coronary atherosclerosis. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2006;26:2523–2529. - PubMed
-
- Stafforini DM, Tjoelker LW, McCormick SP. Molecular basis of the interaction between plasma platelet-activating factor acetylhydrolase and low density lipoprotein. J Biol Chem. 1999;274:7018–7024. - PubMed
-
- Rosenson RS, Hislop C, McConnell D, for the PLASMA Investigators Effects of 1-H-indole-3-glyoxamide (A-002) on concentration of secretory phospholipase A2 (PLASMA study): a phase II double-blind, randomised, placebo-controlled trial. Lancet. 2009;373:649–658. - PubMed
-
- Corson MA. Phospholipase A2 inhibitors in atherosclerosis: the race is on. Lancet. 2009;373:608–610. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- MC_U137686851/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- G0601284/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- RG/08/008/25291/BHF_/British Heart Foundation/United Kingdom
- G0600705/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- RG/08/014/24067/BHF_/British Heart Foundation/United Kingdom
- RG/08/014/BHF_/British Heart Foundation/United Kingdom
- G0401527/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- MC_U137686853/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- MC_U105260792/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- G0801566/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

