Corneal confocal microscopy: a novel noninvasive test to diagnose and stratify the severity of human diabetic neuropathy
- PMID: 20435796
- PMCID: PMC2909064
- DOI: 10.2337/dc10-0253
Corneal confocal microscopy: a novel noninvasive test to diagnose and stratify the severity of human diabetic neuropathy
Abstract
Objective: The accurate quantification of human diabetic neuropathy is important to define at-risk patients, anticipate deterioration, and assess new therapies.
Research design and methods: A total of 101 diabetic patients and 17 age-matched control subjects underwent neurological evaluation, neurophysiology tests, quantitative sensory testing, and evaluation of corneal sensation and corneal nerve morphology using corneal confocal microscopy (CCM).
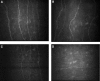
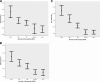
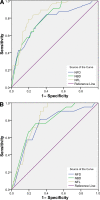
Results: Corneal sensation decreased significantly (P = 0.0001) with increasing neuropathic severity and correlated with the neuropathy disability score (NDS) (r = 0.441, P < 0.0001). Corneal nerve fiber density (NFD) (P < 0.0001), nerve fiber length (NFL), (P < 0.0001), and nerve branch density (NBD) (P < 0.0001) decreased significantly with increasing neuropathic severity and correlated with NDS (NFD r = -0.475, P < 0.0001; NBD r = -0.511, P < 0.0001; and NFL r = -0.581, P < 0.0001). NBD and NFL demonstrated a significant and progressive reduction with worsening heat pain thresholds (P = 0.01). Receiver operating characteristic curve analysis for the diagnosis of neuropathy (NDS >3) defined an NFD of <27.8/mm(2) with a sensitivity of 0.82 (95% CI 0.68-0.92) and specificity of 0.52 (0.40-0.64) and for detecting patients at risk of foot ulceration (NDS >6) defined a NFD cutoff of <20.8/mm(2) with a sensitivity of 0.71 (0.42-0.92) and specificity of 0.64 (0.54-0.74).
Conclusions: CCM is a noninvasive clinical technique that may be used to detect early nerve damage and stratify diabetic patients with increasing neuropathic severity.
Figures
References
-
- Dyck PJ, Norell JE, Tritschler H, Schuette K, Samigullin R, Ziegler D, Bastyr EJ, 3rd, Litchy WJ, O'Brien PC. Challenges in design of multicenter trials: end points assessed longitudinally for change and monotonicity. Diabetes Care 2007;30:2619–2625 - PubMed
-
- Umapathi T, Tan WL, Loke SC, Soon PC, Tavintharan S, Chan YH. Intraepidermal nerve fiber density as a marker of early diabetic neuropathy. Muscle Nerve 2007;35:591–598 - PubMed
-
- Løseth S, Stålberg E, Jorde R, Mellgren SI. Early diabetic neuropathy: thermal thresholds and intraepidermal nerve fibre density in patients with normal nerve conduction studies. J Neurol 2008;255:1197–1202 - PubMed
-
- Malik RA, Tesfaye S, Newrick PG, Walker D, Rajbhandari SM, Siddique I, Sharma AK, Boulton AJ, King RH, Thomas PK, Ward JD. Sural nerve pathology in diabetic patients with minimal but progressive neuropathy. Diabetologia 2005;48:578–585 - PubMed
-
- Malik RA, Veves A, Walker D, Siddique I, Lye RH, Schady W, Boulton AJ. Sural nerve fibre pathology in diabetic patients with mild neuropathy: relationship to pain, quantitative sensory testing and peripheral nerve electrophysiology. Acta Neuropathol 2001;101:367–374 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

