Each conserved active site tyr in the three subunits of human isocitrate dehydrogenase has a different function
- PMID: 20435888
- PMCID: PMC2898308
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M110.115386
Each conserved active site tyr in the three subunits of human isocitrate dehydrogenase has a different function
Abstract
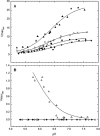
The human NAD-dependent isocitrate dehydrogenase (IDH) is a heterotetrameric mitochondrial enzyme with 2alpha:1beta:1gamma subunit ratio. The three subunits share 40-52% identity in amino acid sequence and each includes a tyrosine in a comparable position: alphaY126, betaY137, and gammaY135. To study the role of the corresponding tyrosines of each of the subunits of human NAD-IDH, the tyrosines were mutated (one subunit at a time) to Ser, Phe, or Glu. Enzymes were expressed with one mutant and two wild-type subunits. The results of characterization of the mutant enzymes suggest that betaY137 is involved in NAD binding and allosteric activation by ADP. The alphaY126 is required for catalytic activity and likely acts as a general acid in the reaction. The gammaY135 is also required for catalytic activity and may be involved in proper folding of the enzyme. The corresponding tyrosines in the three dissimilar subunits of NAD-IDH thus have distinctive functions.
Figures



References
-
- Ramachandran N., Colman R. F. (1980) J. Biol. Chem. 255, 8859–8864 - PubMed
-
- Ehrlich R. S., Colman R. F. (1981) J. Biol. Chem. 256, 1276–1282 - PubMed
-
- Ehrlich R. S., Hayman S., Ramachandran N., Colman R. F. (1981) J. Biol. Chem. 256, 10560–10564 - PubMed
-
- Cohen P. F., Colman R. F. (1972) Biochemistry 11, 1501–1508 - PubMed
-
- Ehrlich R. S., Colman R. F. (1982) J. Biol. Chem. 257, 4769–4774 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

