Metabolic oxidation regulates embryonic stem cell differentiation
- PMID: 20436487
- PMCID: PMC2873061
- DOI: 10.1038/nchembio.364
Metabolic oxidation regulates embryonic stem cell differentiation
Abstract
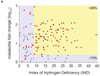
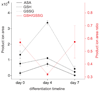
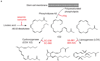
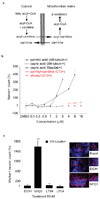
Metabolites offer an important unexplored complementary approach to understanding the pluripotency of stem cells. Using MS-based metabolomics, we show that embryonic stem cells are characterized by abundant metabolites with highly unsaturated structures whose levels decrease upon differentiation. By monitoring the reduced and oxidized glutathione ratio as well as ascorbic acid levels, we demonstrate that the stem cell redox status is regulated during differentiation. On the basis of the oxidative biochemistry of the unsaturated metabolites, we experimentally manipulated specific pathways in embryonic stem cells while monitoring the effects on differentiation. Inhibition of the eicosanoid signaling pathway promoted pluripotency and maintained levels of unsaturated fatty acids. In contrast, downstream oxidized metabolites (for example, neuroprotectin D1) and substrates of pro-oxidative reactions (for example, acyl-carnitines), promoted neuronal and cardiac differentiation. We postulate that the highly unsaturated metabolome sustained by stem cells allows them to differentiate in response to in vivo oxidative processes such as inflammation.
Figures


References
-
- Azuara V, et al. Chromatin signatures of pluripotent cell lines. Nat Cell Biol. 2006;8:532–538. - PubMed
-
- Bernstein BE, et al. A bivalent chromatin structure marks key developmental genes in embryonic stem cells. Cell. 2006;125:315–326. - PubMed
-
- Graumann J, et al. Stable isotope labeling by amino acids in cell culture (SILAC) and proteome quantitation of mouse embryonic stem cells to a depth of 5,111 proteins. Mol Cell Proteomics. 2008;7:672–683. - PubMed
-
- Foss EJ, et al. Genetic basis of proteome variation in yeast. Nat Genet. 2007;39:1369–1375. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

