Factors affecting recruitment and retention of community health workers in a newborn care intervention in Bangladesh
- PMID: 20438642
- PMCID: PMC2875202
- DOI: 10.1186/1478-4491-8-12
Factors affecting recruitment and retention of community health workers in a newborn care intervention in Bangladesh
Abstract
Background: Well-trained and highly motivated community health workers (CHWs) are critical for delivery of many community-based newborn care interventions. High rates of CHW attrition undermine programme effectiveness and potential for implementation at scale. We investigated reasons for high rates of CHW attrition in Sylhet District in north-eastern Bangladesh.
Methods: Sixty-nine semi-structured questionnaires were administered to CHWs currently working with the project, as well as to those who had left. Process documentation was also carried out to identify project strengths and weaknesses, which included in-depth interviews, focus group discussions, review of project records (i.e. recruitment and resignation), and informal discussion with key project personnel.
Results: Motivation for becoming a CHW appeared to stem primarily from the desire for self-development, to improve community health, and for utilization of free time. The most common factors cited for continuing as a CHW were financial incentive, feeling needed by the community, and the value of the CHW position in securing future career advancement. Factors contributing to attrition included heavy workload, night visits, working outside of one's home area, familial opposition and dissatisfaction with pay.
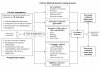
Conclusions: The framework presented illustrates the decision making process women go through when deciding to become, or continue as, a CHW. Factors such as job satisfaction, community valuation of CHW work, and fulfilment of pre-hire expectations all need to be addressed systematically by programs to reduce rates of CHW attrition.
Figures
References
-
- Lehmann U, Sanders D. Community Health Workers: What do we know about them? The state of the evidence on programmes, activities, costs and impact on health outcomes of using community health workers. Geneva: World Health Organization; 2007.
-
- Knippenberg R, Lawn JE, Darmstadt GL, Begkoyian G, Fogstad H, Walelign N, Paul VK. Systematic scaling up of neonatal care in countries. Lancet. 2005;365:1087–1098. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical