Models of accelerated sarcopenia: critical pieces for solving the puzzle of age-related muscle atrophy
- PMID: 20438881
- PMCID: PMC3788572
- DOI: 10.1016/j.arr.2010.04.004
Models of accelerated sarcopenia: critical pieces for solving the puzzle of age-related muscle atrophy
Abstract
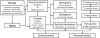
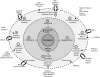
Sarcopenia, the age-related loss of skeletal muscle mass, is a significant public health concern that continues to grow in relevance as the population ages. Certain conditions have the strong potential to coincide with sarcopenia to accelerate the progression of muscle atrophy in older adults. Among these conditions are co-morbid diseases common to older individuals such as cancer, kidney disease, diabetes, and peripheral artery disease. Furthermore, behaviors such as poor nutrition and physical inactivity are well-known to contribute to sarcopenia development. However, we argue that these behaviors are not inherent to the development of sarcopenia but rather accelerate its progression. In the present review, we discuss how these factors affect systemic and cellular mechanisms that contribute to skeletal muscle atrophy. In addition, we describe gaps in the literature concerning the role of these factors in accelerating sarcopenia progression. Elucidating biochemical pathways related to accelerated muscle atrophy may allow for improved discovery of therapeutic treatments related to sarcopenia.
Copyright © 2010 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Adams GR, Vaziri ND. Skeletal muscle dysfunction in chronic renal failure: effects of exercise. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2006;290:F753–61. - PubMed
-
- Adey D, Kumar R, McCarthy JT, Nair KS. Reduced synthesis of muscle proteins in chronic renal failure. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2000;278:E219–25. - PubMed
-
- Adhihetty PJ, O'Leary MF, Chabi B, Wicks KL, Hood DA. Effect of denervation on mitochondrially mediated apoptosis in skeletal muscle. J Appl Physiol. 2007;102:1143–1151. - PubMed
-
- Anker SD, Ponikowski PP, Clark AL, Leyva F, Rauchhaus M, Kemp M, Teixeira MM, Hellewell PG, Hooper J, Poole-Wilson PA, Coats AJ. Cytokines and neurohormones relating to body composition alterations in the wasting syndrome of chronic heart failure. Eur Heart J. 1999;20:683–693. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

