Continued inhibition of structural damage over 2 years in patients with rheumatoid arthritis treated with rituximab in combination with methotrexate
- PMID: 20439295
- PMCID: PMC2935326
- DOI: 10.1136/ard.2009.119222
Continued inhibition of structural damage over 2 years in patients with rheumatoid arthritis treated with rituximab in combination with methotrexate
Erratum in
- Ann Rheum Dis. 2011 Aug;70(8):1519
Abstract
Background: Rituximab inhibited structural damage at 1 year in patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA) who had had a previous inadequate response to tumour necrosis factor (TNF) inhibitors.
Objective: To assess structural damage progression through 2 years.
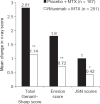
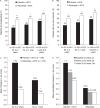
Methods: Intention-to-treat patients with one post-baseline radiograph (rituximab n=281; placebo n=187) received background methotrexate (MTX) and were randomised to rituximab (2 x 1000 mg infusions, 2 weeks apart) or placebo; patients were eligible for rituximab re-treatment every 6 months. By week 104, 82% of the placebo population had received > or = 1 dose of rituximab. Radiographic end points included the change in total Sharp score (TSS), erosion and joint space narrowing scores at week 104.
Results: At week 104, significantly lower changes in TSS (1.14 vs 2.81; p<0.0001), erosion score (0.72 vs 1.80; p<0.0001) and joint space narrowing scores (0.42 vs 1.00; p<0.0009) were observed with rituximab plus MTX vs placebo plus MTX. Within the rituximab group, 87% who had no progression of joint damage at 1 year remained non-progressive at 2 years.
Conclusions: Rituximab plus MTX demonstrated significant and sustained effects on joint damage progression in patients with RA and a previously inadequate response to TNF inhibitors.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Pincus T, Callahan LF. The ‘side effects’ of rheumatoid arthritis: joint destruction, disability and early mortality. Br J Rheumatol 1993;32(Suppl 1):28–37 - PubMed
-
- Pincus T, Callahan LF, Sale WG, et al. Severe functional declines, work disability, and increased mortality in seventy-five rheumatoid arthritis patients studied over nine years. Arthritis Rheum 1984;27:864–72 - PubMed
-
- Breedveld FC, Weisman MH, Kavanaugh AF, et al. The PREMIER study: a multicenter, randomized, double-blind clinical trial of combination therapy with adalimumab plus methotrexate versus methotrexate alone or adalimumab alone in patients with early, aggressive rheumatoid arthritis who had not had previous methotrexate treatment. Arthritis Rheum 2006;54:26–37 - PubMed
-
- St Clair EW, van der Heijde DM, Smolen JS, et al. Combination of infliximab and methotrexate therapy for early rheumatoid arthritis: a randomized, controlled trial. Arthritis Rheum 2004;50:3432–43 - PubMed
-
- Klareskog L, van der Heijde D, de Jager JP, et al. Therapeutic effect of the combination of etanercept and methotrexate compared with each treatment alone in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: double-blind randomised controlled trial. Lancet 2004;363:675–81 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

