Risperidone administered during asymptomatic period of adolescence prevents the emergence of brain structural pathology and behavioral abnormalities in an animal model of schizophrenia
- PMID: 20439320
- PMCID: PMC3196943
- DOI: 10.1093/schbul/sbq040
Risperidone administered during asymptomatic period of adolescence prevents the emergence of brain structural pathology and behavioral abnormalities in an animal model of schizophrenia
Abstract
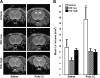
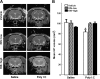
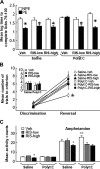
Schizophrenia is a disorder of a neurodevelopmental origin manifested symptomatically after puberty. Structural neuroimaging studies show that neuroanatomical aberrations precede onset of symptoms, raising a question of whether schizophrenia can be prevented. Early treatment with atypical antipsychotics may reduce the risk of transition to psychosis, but it remains unknown whether neuroanatomical abnormalities can be prevented. We have recently shown, using in vivo structural magnetic resonance imaging, that treatment with the atypical antipsychotic clozapine during an asymptomatic period of adolescence prevents the emergence of schizophrenia-like brain structural abnormalities in adult rats exposed to prenatal immune challenge, in parallel to preventing behavioral abnormalities. Here we assessed the preventive efficacy of the atypical antipsychotic risperidone (RIS). Pregnant rats were injected on gestational day 15 with the viral mimic polyriboinosinic-polyribocytidylic acid (poly I:C) or saline. Their male offspring received daily RIS (0.045 or 1.2 mg/kg) or vehicle injection in peri-adolescence (postnatal days [PND] 34-47). Structural brain changes and behavior were assessed at adulthood (from PND 90). Adult offspring of poly I:C-treated dams exhibited hallmark structural abnormalities associated with schizophrenia, enlarged lateral ventricles and smaller hippocampus. Both of these abnormalities were absent in the offspring of poly I:C dams that received RIS at peri-adolescence. This was paralleled by prevention of schizophrenia-like behavioral abnormalities, attentional deficit, and hypersensitivity to amphetamine in these offspring. We conclude that pharmacological intervention during peri-adolescence can prevent the emergence of behavioral abnormalities and brain structural pathology resulting from in utero insult. Furthermore, highly selective 5HT(2A) receptor antagonists may be promising targets for psychosis prevention.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Clozapine administration in adolescence prevents postpubertal emergence of brain structural pathology in an animal model of schizophrenia.Biol Psychiatry. 2009 Dec 1;66(11):1038-46. doi: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2009.07.005. Epub 2009 Sep 2. Biol Psychiatry. 2009. PMID: 19726031
-
Tracing the development of psychosis and its prevention: what can be learned from animal models.Neuropharmacology. 2012 Mar;62(3):1273-89. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2011.04.019. Epub 2011 Jun 23. Neuropharmacology. 2012. PMID: 21703648 Review.
-
Effects of risperidone and paliperidone pre-treatment on locomotor response following prenatal immune activation.J Psychiatr Res. 2011 Sep;45(9):1194-201. doi: 10.1016/j.jpsychires.2011.02.007. Epub 2011 Mar 25. J Psychiatr Res. 2011. PMID: 21440257 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of risperidone treatment in adolescence on hippocampal neurogenesis, parvalbumin expression, and vascularization following prenatal immune activation in rats.Brain Behav Immun. 2012 Feb;26(2):353-63. doi: 10.1016/j.bbi.2011.11.004. Epub 2011 Nov 30. Brain Behav Immun. 2012. PMID: 22154704
-
Serotonin and dopamine interactions in psychosis prevention.Prog Brain Res. 2008;172:141-53. doi: 10.1016/S0079-6123(08)00907-2. Prog Brain Res. 2008. PMID: 18772031 Review.
Cited by
-
Behavioral, pharmacological, and immunological abnormalities after streptococcal exposure: a novel rat model of Sydenham chorea and related neuropsychiatric disorders.Neuropsychopharmacology. 2012 Aug;37(9):2076-87. doi: 10.1038/npp.2012.56. Epub 2012 Apr 25. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2012. PMID: 22534626 Free PMC article.
-
Corresponding decrease in neuronal markers signals progressive parvalbumin neuron loss in MAM schizophrenia model.Int J Neuropsychopharmacol. 2014 Oct;17(10):1609-19. doi: 10.1017/S146114571400056X. Epub 2014 Apr 30. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol. 2014. PMID: 24787547 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of paliperidone and risperidone on extracellular glutamate in the prefrontal cortex of rats exposed to prenatal immune activation or MK-801.Neurosci Lett. 2011 Aug 18;500(3):167-71. doi: 10.1016/j.neulet.2011.06.011. Epub 2011 Jun 15. Neurosci Lett. 2011. PMID: 21699956 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of prenatal immune activation and peri-adolescent stress on amphetamine-induced conditioned place preference in the rat.Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2012 Jul;222(2):313-24. doi: 10.1007/s00213-012-2646-8. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2012. PMID: 22290326 Free PMC article.
-
Evolution of structural abnormalities in the rat brain following in utero exposure to maternal immune activation: A longitudinal in vivo MRI study.Brain Behav Immun. 2017 Jul;63:50-59. doi: 10.1016/j.bbi.2016.12.008. Epub 2016 Dec 9. Brain Behav Immun. 2017. PMID: 27940258 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Pantelis C, Yucel M, Wood SJ, et al. Structural brain imaging evidence for multiple pathological processes at different stages of brain development in schizophrenia. Schizophr Bull. 2005;31:672–696. - PubMed
-
- Job DE, Whalley HC, Johnstone EC, Lawrie SM. Grey matter changes over time in high risk subjects developing schizophrenia. Neuroimage. 2005;25:1023–1030. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

