Smooth and cardiac muscle-selective knock-out of Kruppel-like factor 4 causes postnatal death and growth retardation
- PMID: 20439457
- PMCID: PMC2898332
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M110.112482
Smooth and cardiac muscle-selective knock-out of Kruppel-like factor 4 causes postnatal death and growth retardation
Abstract
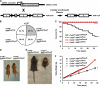
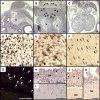
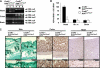
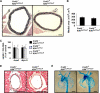
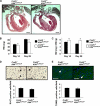
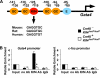
Krüppel-like factor 4 (Klf4) is a transcription factor involved in differentiation and proliferation in multiple tissues. We demonstrated previously that tamoxifen-induced deletion of the Klf4 gene in mice accelerated neointimal formation but delayed down-regulation of smooth muscle cell differentiation markers in carotid arteries following injury. To further determine the role of Klf4 in the cardiovascular system, we herein derived mice deficient for the Klf4 gene in smooth and cardiac muscle using the SM22alpha promoter (SM22alpha-CreKI(+)/Klf4(loxP/loxP) mice). SM22alpha-CreKI(+)/Klf4(loxP/loxP) mice were born at the expected Mendelian ratio, but they gradually died after birth. Although approximately 40% of SM22alpha-CreKI(+)/Klf4(loxP/loxP) mice survived beyond postnatal day 28, they exhibited marked growth retardation. In wild-type mice, Klf4 was expressed in the heart from late embryonic development through adulthood, whereas it was not expressed in smooth muscle. No changes were observed in morphology or expression of smooth muscle cell differentiation markers in vessels of SM22alpha-CreKI(+)/Klf4(loxP/loxP) mice. Of interest, cardiac output was significantly decreased in SM22alpha-CreKI(+)/Klf4(loxP/loxP) mice, as determined by magnetic resonance imaging. Moreover, a lack of Klf4 in the heart resulted in the reduction in expression of multiple cardiac genes, including Gata4. In vivo chromatin immunoprecipitation assays on the heart revealed that Klf4 bound to the promoter region of the Gata4 gene. Results provide novel evidence that Klf4 plays a key role in late fetal and/or postnatal cardiac development.
Figures

References
-
- Segre J. A., Bauer C., Fuchs E. (1999) Nat. Genet. 22, 356–360 - PubMed
-
- Katz J. P., Perreault N., Goldstein B. G., Actman L., McNally S. R., Silberg D. G., Furth E. E., Kaestner K. H. (2005) Gastroenterology 128, 935–945 - PubMed
-
- Takahashi K., Tanabe K., Ohnuki M., Narita M., Ichisaka T., Tomoda K., Yamanaka S. (2007) Cell 131, 861–872 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

