Phosphorylation of mixed lineage leukemia 5 by CDC2 affects its cellular distribution and is required for mitotic entry
- PMID: 20439461
- PMCID: PMC2898323
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M109.098558
Phosphorylation of mixed lineage leukemia 5 by CDC2 affects its cellular distribution and is required for mitotic entry
Abstract
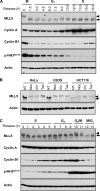
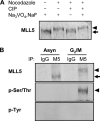
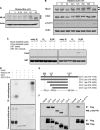
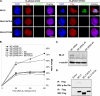
The human mixed lineage leukemia-5 (MLL5) gene is frequently deleted in myeloid malignancies. Emerging evidence suggests that MLL5 has important functions in adult hematopoiesis and the chromatin regulatory network, and it participates in regulating the cell cycle machinery. Here, we demonstrate that MLL5 is tightly regulated through phosphorylation on its central domain at the G(2)/M phase of the cell cycle. Upon entry into mitosis, the phosphorylated MLL5 delocalizes from condensed chromosomes, whereas after mitotic exit, MLL5 becomes dephosphorylated and re-associates with the relaxed chromatin. We further identify that the mitotic phosphorylation and subcellular localization of MLL5 are dependent on Cdc2 kinase activity, and Thr-912 is the Cdc2-targeting site. Overexpression of the Cdc2-targeting MLL5 fragment obstructs mitotic entry by competitive inhibition of the phosphorylation of endogenous MLL5. In addition, G(2) phase arrest caused by depletion of endogenous MLL5 can be compensated by exogenously overexpressed full-length MLL5 but not the phosphodomain deletion or MLL5-T912A mutant. Our data provide evidence that MLL5 is a novel cellular target of Cdc2, and the phosphorylation of MLL5 may have an indispensable role in the mitotic progression.
Figures



References
-
- Hasle H., Aricò M., Basso G., Biondi A., Cantù Rajnoldi A., Creutzig U., Fenu S., Fonatsch C., Haas O. A., Harbott J., Kardos G., Kerndrup G., Mann G., Niemeyer C. M., Ptoszkova H., Ritter J., Slater R., Starý J., Stollmann-Gibbels B., Testi A. M., van Wering E. R., Zimmermann M. (1999) Leukemia 13, 376–385 - PubMed
-
- Brezinová J., Zemanová Z., Ransdorfová S., Pavlistová L., Babická L., Housková L., Melichercíková J., Sisková M., Cermák J., Michalová K. (2007) Cancer Genet. Cytogenet. 173, 10–16 - PubMed
-
- Luna-Fineman S., Shannon K. M., Lange B. J. (1995) Blood 85, 1985–1999 - PubMed
-
- Johnson E. J., Scherer S. W., Osborne L., Tsui L. C., Oscier D., Mould S., Cotter F. E. (1996) Blood 87, 3579–3586 - PubMed
-
- Le Beau M. M., Espinosa R., 3rd, Davis E. M., Eisenbart J. D., Larson R. A., Green E. D. (1996) Blood 88, 1930–1935 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

