The structure of Neisseria meningitidis lipid A determines outcome in experimental meningococcal disease
- PMID: 20439476
- PMCID: PMC2897371
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.01311-09
The structure of Neisseria meningitidis lipid A determines outcome in experimental meningococcal disease
Abstract
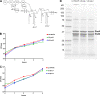
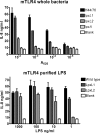
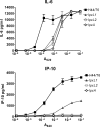
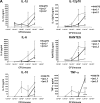
Lipopolysaccharide (LPS), a major component of the meningococcal outer membrane, is sensed by the host through activation of Toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4). Recently, we demonstrated that a surprisingly large fraction of Neisseria meningitidis disease isolates are lipid A mutants, due to inactivating mutations in the lpxL1 gene. The lpxL1 mutants activate human TLR4 much less efficiently than wild-type bacteria, which may be advantageous by allowing them to escape from the innate immune system. Here we investigated the influence of lipid A structure on virulence in a mouse model of meningococcal sepsis. One limitation, however, is that murine TLR4 recognizes lpxL1 mutant bacteria much better than human TLR4. We show that an lpxL2 mutant, another lipid A mutant lacking an acyl chain at a different position, activates murine TLR4 less efficiently than the lpxL1 mutant. Therefore, the lpxL2 mutant in mice might be a better model for infections with lpxL1 mutants in humans. Interestingly, we found that the lpxL2 mutant is more virulent in mice than the wild-type strain, whereas the lpxL1 mutant is actually much less virulent than the wild-type strain. These results demonstrate the crucial role of N. meningitidis lipid A structure in virulence.
Figures



References
-
- Akashi, S., Y. Nagai, H. Ogata, M. Oikawa, K. Fukase, S. Kusumoto, K. Kawasaki, M. Nishijima, S. Hayashi, M. Kimoto, and K. Miyake. 2001. Human MD-2 confers on mouse Toll-like receptor 4 species-specific lipopolysaccharide recognition. Int. Immunol. 13:1595-1599. - PubMed
-
- An, H., H. Xu, Y. Yu, M. Zhang, R. Qi, X. Yan, S. Liu, W. Wang, Z. Guo, Z. Qin, and X. Cao. 2002. Up-regulation of TLR9 gene expression by LPS in mouse macrophages via activation of NF-kappaB, ERK and p38 MAPK signal pathways. Immunol. Lett. 81:165-169. - PubMed
-
- Banus, H. A., R. J. Vandebriel, R. H. de, J. A. Dormans, N. J. Nagelkerke, F. R. Mooi, B. Hoebee, H. J. van Kranen, and T. G. Kimman. 2006. Host genetics of Bordetella pertussis infection in mice: significance of Toll-like receptor 4 in genetic susceptibility and pathobiology. Infect. Immun. 74:2596-2605. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bernheiden, M., J. M. Heinrich, G. Minigo, C. Schutt, F. Stelter, M. Freeman, D. Golenbock, and R. S. Jack. 2001. LBP, CD14, TLR4 and the murine innate immune response to a peritoneal Salmonella infection. J. Endotoxin Res. 7:447-450. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

