Regulation of learning and memory by meningeal immunity: a key role for IL-4
- PMID: 20439540
- PMCID: PMC2867291
- DOI: 10.1084/jem.20091419
Regulation of learning and memory by meningeal immunity: a key role for IL-4
Abstract
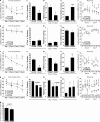
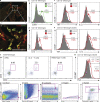
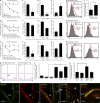
Proinflammatory cytokines have been shown to impair cognition; consequently, immune activity in the central nervous system was considered detrimental to cognitive function. Unexpectedly, however, T cells were recently shown to support learning and memory, though the underlying mechanism was unclear. We show that one of the steps in the cascade of T cell-based support of learning and memory takes place in the meningeal spaces. Performance of cognitive tasks led to accumulation of IL-4-producing T cells in the meninges. Depletion of T cells from meningeal spaces skewed meningeal myeloid cells toward a proinflammatory phenotype. T cell-derived IL-4 was critical, as IL-4(-/-) mice exhibited a skewed proinflammatory meningeal myeloid cell phenotype and cognitive deficits. Transplantation of IL-4(-/-) bone marrow into irradiated wild-type recipients also resulted in cognitive impairment and proinflammatory skew. Moreover, adoptive transfer of T cells from wild-type into IL-4(-/-) mice reversed cognitive impairment and attenuated the proinflammatory character of meningeal myeloid cells. Our results point to a critical role for T cell-derived IL-4 in the regulation of cognitive function through meningeal myeloid cell phenotype and brain-derived neurotrophic factor expression. These findings might lead to the development of new immune-based therapies for cognitive impairment associated with immune decline.
Figures

References
-
- Aharoni R., Eilam R., Domev H., Labunskay G., Sela M., Arnon R. 2005. The immunomodulator glatiramer acetate augments the expression of neurotrophic factors in brains of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis mice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 102:19045–19050 10.1073/pnas.0509438102 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Balschun D., Wetzel W., Del Rey A., Pitossi F., Schneider H., Zuschratter W., Besedovsky H.O. 2004. Interleukin-6: a cytokine to forget. FASEB J. 18:1788–1790 - PubMed
-
- Baune B.T., Ponath G., Rothermundt M., Riess O., Funke H., Berger K. 2008. Association between genetic variants of IL-1beta, IL-6 and TNF-alpha cytokines and cognitive performance in the elderly general population of the MEMO-study. Psychoneuroendocrinology. 33:68–76 10.1016/j.psyneuen.2007.10.002 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

