Whole-genome profiling of mutagenesis in Caenorhabditis elegans
- PMID: 20439774
- PMCID: PMC2881127
- DOI: 10.1534/genetics.110.116616
Whole-genome profiling of mutagenesis in Caenorhabditis elegans
Abstract
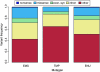
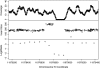
Deep sequencing offers an unprecedented view of an organism's genome. We describe the spectrum of mutations induced by three commonly used mutagens: ethyl methanesulfonate (EMS), N-ethyl-N-nitrosourea (ENU), and ultraviolet trimethylpsoralen (UV/TMP) in the nematode Caenorhabditis elegans. Our analysis confirms the strong GC to AT transition bias of EMS. We found that ENU mainly produces A to T and T to A transversions, but also all possible transitions. We found no bias for any specific transition or transversion in the spectrum of UV/TMP-induced mutations. In 10 mutagenized strains we identified 2723 variants, of which 508 are expected to alter or disrupt gene function, including 21 nonsense mutations and 10 mutations predicted to affect mRNA splicing. This translates to an average of 50 informative mutations per strain. We also present evidence of genetic drift among laboratory wild-type strains derived from the Bristol N2 strain. We make several suggestions for best practice using massively parallel short read sequencing to ensure mutation detection.
Figures


References
-
- Acevedo-Arozena, A., S. Wells, P. Potter, M. Kelly, R. D. Cox et al., 2008. ENU mutagenesis, a way forward to understand gene function. Annu. Rev. Genomics Hum. Genet. 9 49–69. - PubMed
-
- Anderson, K. V., 2000. Finding the genes that direct mammalian development: ENU mutagenesis in the mouse. Trends Genet. 16 99–102. - PubMed
-
- Anderson, P., 1995. Mutagenesis. Methods Cell Biol. 48 31–58. - PubMed
-
- Barstead, R. J., and D. G. Moerman, 2006. C. elegans deletion mutant screening. Methods Mol. Biol. 351 51–58. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

